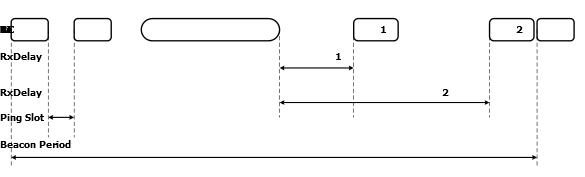
In Class A, the downlink is non-deterministic since it depends on random uplinks from a sleeping end-device. In Class B the end-device reduces the downlink latency by opening periodic downlink receive windows. The periodicity of the downlink windows is maintained by synchronizing the clocks of the end-device and the network server. For the synchronization, the network server commands the gateways to send a beacon at regular intervals. During uplink, the Class B end-device behaves similar to that of a Class A end-device.
A Class B end-device manages to reduce power consumption and yet reduces the downlink latency. The following figure shows the data transmission and reception sequence for a typical Class B end-device.