A Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) takes a data stream of bytes from the NVM (either the entire Flash, only the Boot section, or both the Boot section and the application code section) and generates a checksum. The CRC peripheral (CRCSCAN) can be used to detect errors in the program memory.
The last location in the section to check has to contain the correct pre-calculated 16-bit checksum for comparison. If the checksum calculated by the CRCSCAN and the pre-calculated checksums match, a status bit is set. If they do not match, the Status register (CRCSCAN.STATUS) will indicate that it failed. The user can choose to let the CRCSCAN generate a Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) if the checksums do not match.
An n-bit CRC applied to a data block of arbitrary length will detect any single alteration (error burst) up to n bits in length. For longer error bursts a fraction 1-2-n will be detected.
The CRC generator supports CRC-16-CCITT.
Polynomial:
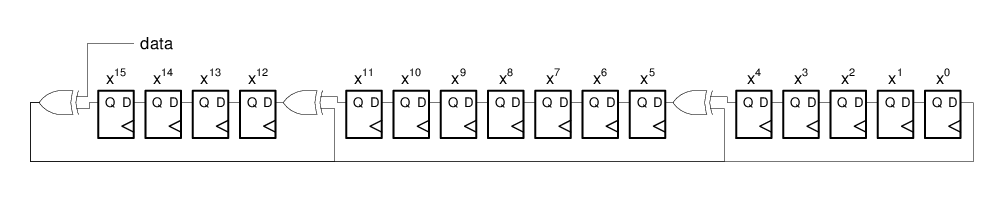
- CRC-16-CCITT: x16 + x12 + x5 + 1
The CRC reads byte-by-byte the content of the section(s) it is set up to check, starting with byte 0, and generates a new checksum per byte. The byte is sent through a shift register as depicted below, starting with the Most Significant bit. If the last bytes in the section contain the correct checksum, the CRC will pass. See Checksum for how to place the checksum. The initial value of the Checksum register is 0xFFFF.