The ADC in Atmel AVR devices can be configured for single-ended or differential conversion. Single-ended mode is used to measure input voltages on a single input channel, while differential mode is used to measure the difference between two channels. Regardless of conversion mode, input voltages on any channel must stay between GND and AVCC.
When using single-ended mode, the voltage relative to GND is converted to a digital value. Using differential channels, the output from a differential amplifier (with an optional gain stage) is converted to a digital value (possibly negative). A simplified illustration of the input circuitry is shown in the figure below.
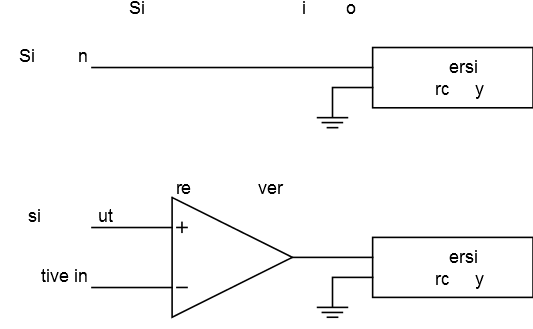
To decide the conversion range, the conversion circuitry needs a voltage reference (VREF) to indicate the voltage level corresponding to the maximum output value. According to the datasheets, VREF should be at least 2.0V for standard devices, while devices operating down to 1.8V can use a reference voltage down to 1.0V. This applies both to single-ended and differential mode. Consult the datasheet for details.