The offset error is defined as the deviation of the actual ADC’s transfer function from the ideal straight line at zero input voltage.
When the transition from output value 0 to 1 does not occur at an input value of ½ LSB, then we say that there is an offset error. With positive offset errors, the output value is larger than 0 when the input voltage approaches ½ LSB from below. With negative offset errors, the input value is larger than ½ LSB when the first output value transition occurs. In other words, if the actual transfer function lies below the ideal line, there is a negative offset and vice versa. Negative and positive offsets are shown in Figure below.
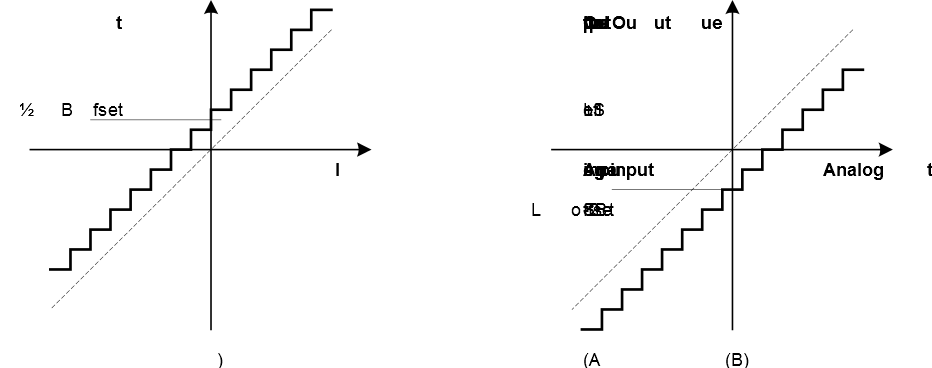
Since single-ended conversion gives positive results only, the offset measurement procedures are different when using single-ended and differential channels.