1.1.9 PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board: Building and Running the CAN Bootloader applications
Downloading and building the application
To clone or download this application from Github,go to the main page of this repository and then click Clone button to clone this repo or download as zip file. This content can also be download using content manager by following these instructions
Path of the application within the repository is apps/can_bootloader/
To build the application, refer to the following table and open the project using its IDE.
Bootloader Application
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| bootloader/firmware/pic32mz_w1_curiosity.X | MPLABX Project for PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board |
Test Application
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| test_app/firmware/pic32mz_w1_curiosity.X | MPLABX Project for PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board |
Setting up PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board
PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board is used for both Host Development kit and Target Development kit
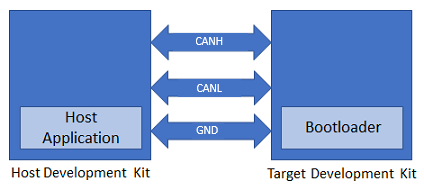
Connect ATA6563 click board to the PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board for each board as per the Pin connections shown below
PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board ATA6563 click board PIN14 (RPB9), mikroBUS Connector RX (PIN 14) PIN3 (RPB7), mikroBUS Connector TX (PIN 13) +3.3V, mikroBUS Connector 3V3 (PIN 7) +5V, mikroBUS Connector 5V (PIN 10) GND, mikroBUS Connector GND (PIN 9) Connect ATA6563 click board-1 to ATA6563 click board-2 using female to female DB9 serial cable
Connect the USB to TTL serial (USB UART click board) to U1TX pin (pin 23) and U1RX pin (pin 13) of J207 header for each board
Connect the Debug USB port on the board to the computer using a mini USB cable for each board
Connect mini USB cable to USB UART click board to the computer for each board (This will enumerate the USB to UART port)
Building and Configuring CAN Host Applications
Using CAN NVM Host application to send the application binary to Target development kit
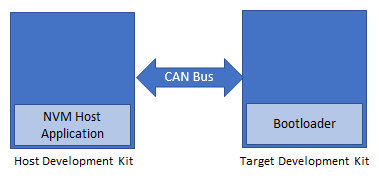
If the NVM Host Development Kit being used is other than PIC32MZ W1 Curiosity Board then follow the steps mentioned in Configuring NVM Host application project
Open the NVM host application project host_app_nvm/firmware/pic32mz_w1_curiosity.X in the IDE
- If a NVM host application project of different development kit is used then open that project in the IDE
Build and program the NVM host application using the IDE on to the Host development kit
- The prebuilt test application image available under host_app_nvm/firmware/src/test_app_images/image_pattern_hex_pic32mz_w1_curiosity.h will be programmed on to the Target development kit with default host_app_nvm project configuration
Jump to Running The Application
Running the Application
Open the bootloader project bootloader/firmware/pic32mz_w1_curiosity.X in the IDE
Build and program the application using the IDE on to the Target development kit
- RED LED will be turned-on to indicate that bootloader code is running on the target
- RED LED will also turn on when the bootloader does not find a valid application; i.e. the first word of the application (stack pointer), contains 0xFFFFFFFF
If the test application is being programmed, Open the Terminal application (Ex.:Tera Term) on the computer and configure the serial port settings for Target Development kit as follows:
- Baud : 115200
- Data : 8 Bits
- Parity : None
- Stop : 1 Bit
- Flow Control : None
Press the Switch SW1 on the Host development kit to trigger programming of the application binary
Once the programming is complete,
RED LED on the Host development kit will be turned on indicating success
The target development kit will be reset. Upon re-start, the boot-loader will jump to the user application
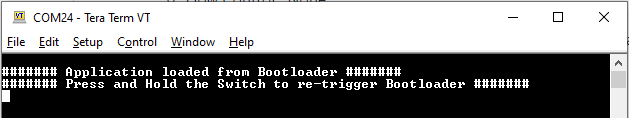
If the test application is programmed then RED LED should start blinking and you should see below output on the Target development kit console
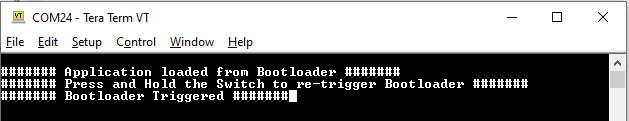
Press and hold the Switch SW1 to trigger Bootloader from test application and you should see below output
Press Reset button on the Host development kit to reprogram the application binary
Repeat Steps 4-5 once
- This step is to verify that bootloader is running after triggering bootloader from test application in Step 6
Additional Steps (Optional)
Using CAN NVM Host application
To bootload any application other than host_app_nvm/firmware/src/test_app_images/image_pattern_hex_pic32mz_w1_curiosity.h refer to Application Configurations
Once the application is configured, Refer to Configuring NVM Host application project for setting up the host_app_nvm project
Once done repeat the applicable steps mentioned in Running The Application
