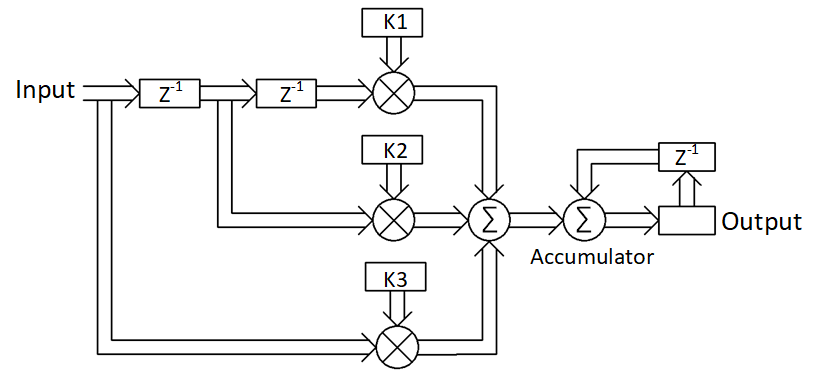
3 PIC Control
In control theory, a PID controller takes the difference between the desired and actual outputs and converts them into three terms: proportional, integral and differential. The proportional term is a simple multiplication of the difference. The integral term is a summation of the current and previous inputs. And, the differential term is the difference between the current and previous inputs. The proportional term drives the output toward a minimal difference between desired and actual outputs. The integral term drives the output toward a zero difference between the desired and actual output by integrating long term non-zero error terms. The differential term acts as a stabilizing factor, which slows the approach to a zero error to prevent overshoot.