Since the aquarium will house live fish, the quality of the water is extremely important. The Atlas Scientific Consumer Grade pH (potential of hydrogen) probe is a sensor that measures the hydrogen ion activity in a liquid. The pH scale (ranging from 1-14) is used to determine the acidity of a substance. When a substance has a pH value of “1”, the substance is considered highly acidic and has the highest amount of hydrogen ions. A pH value of “7” is considered neutral, while a value of “14” is considered highly alkaline and has fewer hydrogen ions. Figure 1 shows common substances and their associated pH values.
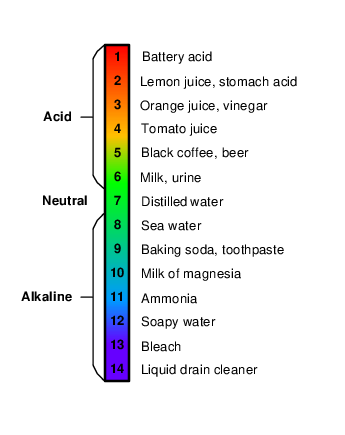
When water has a pH value of “1”, there are one million times more hydrogen ions than if the water had a neutral value of “7”, which is considered “pure” water or water that does not contain dissolved substances. This is due to the fact that a pH value of “1” represents 101 hydrogen ions, while the neutral value of “7” represents 107 hydrogen ions. The difference between a pH of “1” and a pH of “7” is 106, or one million. A pH value of “1” will have ten trillion (1013) times more hydrogen ions than a substance with a pH value of “14”.
The Atlas Scientific probe uses a silver chloride electrode and a reference wire to detect changes in ion activity. The electrode consists of a small, glass membrane constructed of silica glass containing metal salts. Inside of the glass membrane is a silver chloride solution and a silver wire. The reference wire is suspended in a neutral solution. Figure 2 shows the view of the glass electrode suspended in a test liquid.
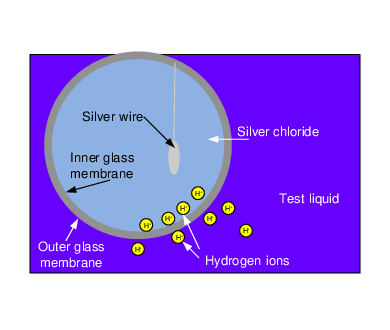
When the probe is placed into a test liquid, an ion exchange occurs between the metal salts on the inside of the glass membrane and the chloride solution. This creates a very small current in the chloride solution. Simultaneously, the test liquid also exchanges ions with the outer surface of the electrode, creating a current in the test liquid. The output of the probe represents the potential difference as an analog voltage signal.