1.1 Console Debug System Service using UART
This example application demonstrates the UART based console and debug system service.
Description
The application example first demonstrates the various debug system service macros. It then demonstrates the console related APIs. The application asks the user to enter a character on the console which is echoed back using the console system service read/write APIs.
Downloading and Building the Application
To clone or download this application from Github, go to the main page of this repository and then click Clone button to clone this repository or download as zip file. This content can also be downloaded using content manager by following these instructions.
Path of the application within the repository is apps/system/console_debug/sys_console_debug_uart_read_write/firmware.
To build the application, refer to the following table and open the project using its IDE.
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pic32cm_jh01_curiosity_pro.X | MPLABX project for PIC32CM JH01 Curiosity Pro Development Board |
Setting Up the Hardware
The following table shows the target hardware for the application projects.
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pic32cm_jh01_curiosity_pro.X | PIC32CM JH01 Curiosity Pro Development Board |
Setting Up PIC32CM JH01 Curiosity Pro Development Board
- Connect the Debug USB port on the board to the computer using a micro USB cable
Running the Application
- Open the Terminal application (Ex.:Tera term) on the computer
- Connect to the EDBG Virtual COM port and configure the serial settings as
follows:
- Baud : 115200
- Data : 8 Bits
- Parity : None
- Stop : 1 Bit
- Flow Control : None
- Build and Program the application using its IDE
- Observe the following output on the terminal
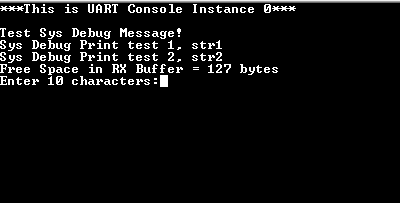
- First few prints demonstrate the output from the debug system service APIs
- It then prints the free space available in the receive buffer
- It then asks the user to enter 10 characters
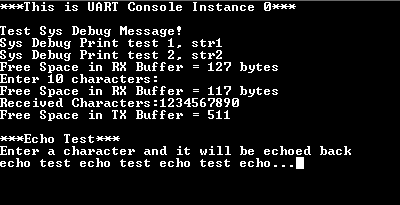
- After entering 10 characters, observe the following output on the terminal

- The output first prints the free space available in the receive buffer
- Since 10 characters are pending to be read out from the receive buffer, the free space in the receive buffer is reduced by 10
- After this, it prints the received characters on the terminal
- Application then waits for the transmit buffer to become empty
- Once empty, the application prints the free space available in the transmit buffer, which should be same as the size of the transmit buffer configured in MHC minus 1
- After this, the demonstration asks the user to enter a character, and echoes it
back on the terminal.
- LED toggles every-time the character is printed on the terminal
| Board | LED Name |
|---|---|
| PIC32CM JH01 Curiosity Pro Development Board | LED0 |
