7.2 Example
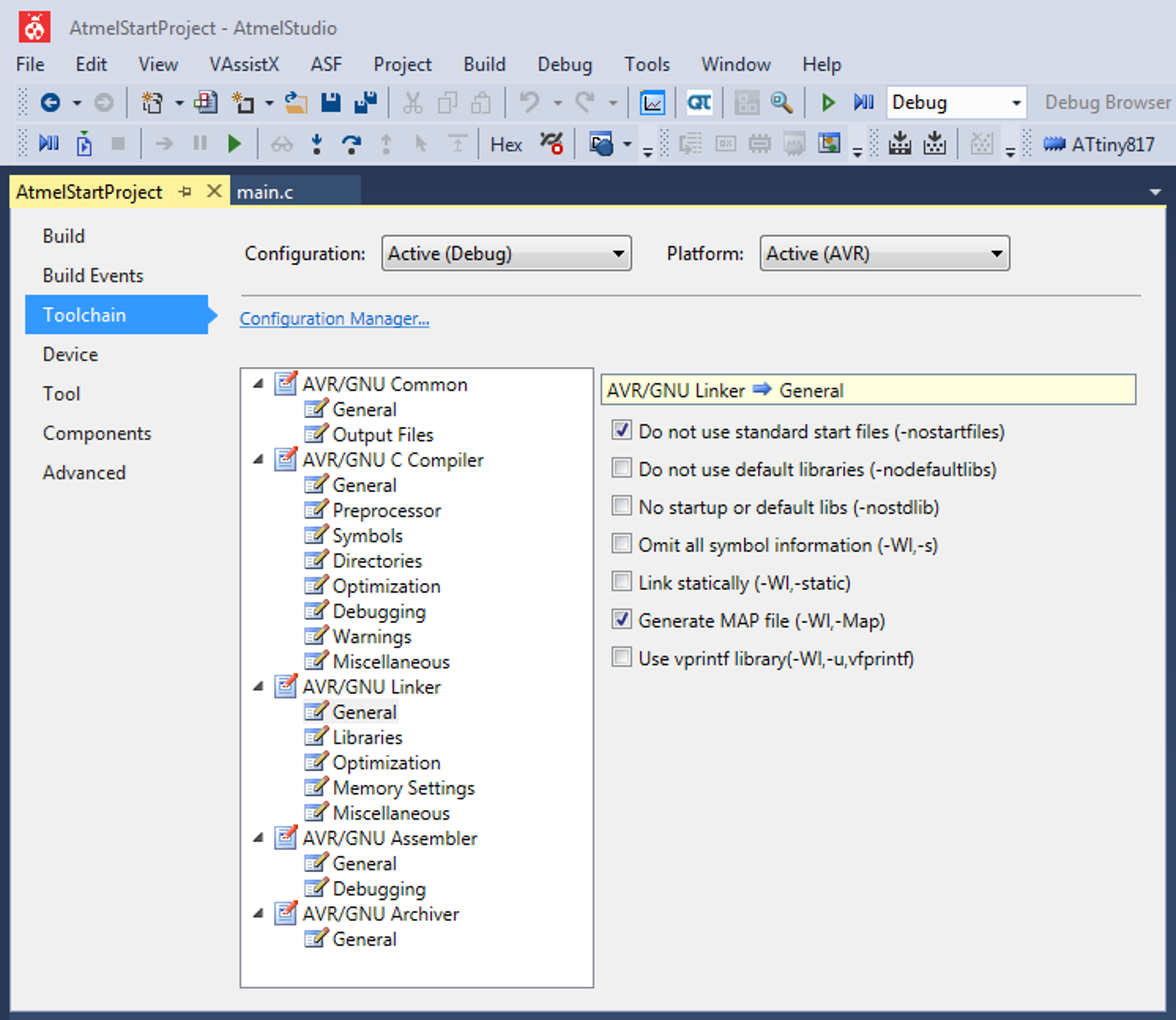
To take advantage of the smaller vector table it is necessary to replace the standard start files used by AVR-GCC. These are disabled by setting the linker flag -nostartfiles when compiling the project. In Atmel Studio 7.0 this can be found in Project Properties (Alt+F7) - Toolchain - AVR/GNU Linker - General, as seen in Figure 7-1.
The following code snippet shows an example for the code needed to replace the standard start files. In a future Toolchain release, this step will not be needed to configure the Compact Vector Table.
// io.h includes the device header file with necessary defines #include <avr/io.h> // Letting the compiler know there will be something called main extern int main(void); // Being nice to the compiler by predeclaring the ISRs void __vector_cvt_nmi(void) __attribute__((weak, alias("dummy_handler"))); void __vector_cvt_lvl1(void) __attribute__((weak, alias("dummy_handler"))); void __vector_cvt_lvl0(void) __attribute__((weak, alias("dummy_handler"))); // Setting up the vector section // The rjmp instruction can handle 8k code space, so this is used for // vector tables on devices with 8k flash or smaller. Other devices // use the jmp instruction. __attribute__((section(".vectors"), naked)) void vectors(void) { #if (PROGMEM_SIZE <= 0x2000) asm("rjmp __ctors_end"); asm("rjmp __vector_cvt_nmi"); asm("rjmp __vector_cvt_lvl1"); asm("rjmp __vector_cvt_lvl0"); #else asm("jmp __ctors_end"); asm("jmp __vector_cvt_nmi"); asm("jmp __vector_cvt_lvl1"); asm("jmp __vector_cvt_lvl0"); #endif } // Initialize the AVR core __attribute__((section(".init2"), naked)) void init2(void) { // GCC expects r1 to be zero asm("clr r1"); // Make sure the status register has a known state SREG = 0; // Point the stack pointer to the end of stack SPL = INTERNAL_SRAM_END & 0xff; // (low byte) SPH = (INTERNAL_SRAM_END >> 8); // (high byte) } // Handling main __attribute__((section(".init9"), naked)) void init9(void) { main(); // Jump to avr libc defined exit handler // (Disables interrupts and runs an empty loop forever) asm("jmp _exit"); } // Dummy handler alias for unused ISRs void dummy_handler(void) { while (1) ; }
The following code snippet shows an example on how to configure the Compact Vector Table, using the interrupt vector names defined in the example start-up code from above.
// io.h includes the device header file with register and vector defines, // it also includes xmega.h, containing the CCP macro _PROTECTED_WRITE(). #include <avr/io.h> // interrupt.h contains the ISR related content #include <avr/interrupt.h> void compact_vector_table_example(void) { // Set the Compact Vector Table // read-modify-write to preserve other configured bits _PROTECTED_WRITE(CPUINT.CTRLA, (CPUINT.CTRLA | CPUINT_CVT_bm)); //Enable global interrupts sei(); } ISR(__vector_cvt_lvl0) { // All level 0 interrupt will be handled here if (PORTA.INTFLAGS) { // Example on how to handle PORTA interrupts in CVT mode } } ISR(__vector_cvt_lvl1) { // If enabled, level 1 interrupt will be handled here } ISR(__vector_cvt_nmi) { // If enabled, NMI interrupts will be handled here }
Atmel | START example
A use case example for Compact Vector Table using Atmel | START is also available. For more information, see the Get Source Code from Atmel | START chapter.
