1.1 TCP/IP IPERF Application
Iperf is a tool for the measurement of maximum achievable throughput of a network device on IP networks
The Iperf demo creates an application to run Iperf on target board and measure the network performance.
Description
The TCP/IP IPERF Application is based on MPLAB® Harmony 3 TCP/IP Stack.
The Harmony TCP/IP stack is a collection of different network protocols.
The source files of Harmony 3 TCP/IP stack is available here.
The demo is created with MPLAB X IDE and MCC plugin.
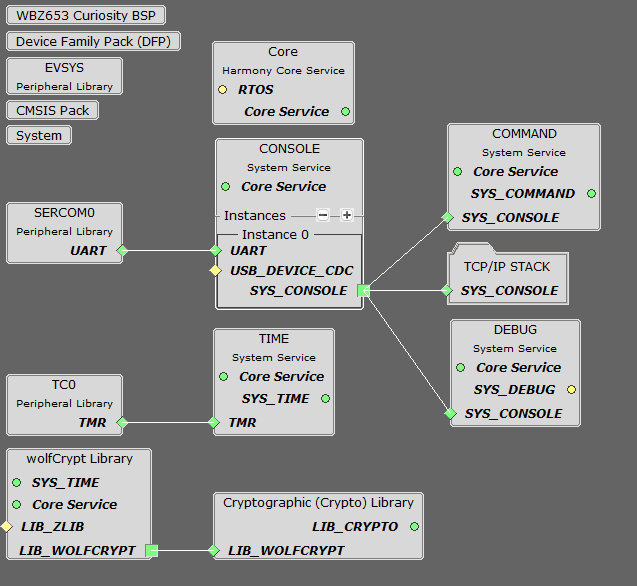
MCC Project Graph - TCP/IP IPERF Application
The following Project Graph shows the Harmony components included in the TCP/IP IPERF demo application.
TCP/IP Configuration - TCP/IP IPERF Application
The TCP/IP modules enabled for the demo is shown in the TCP/IP Configuration Overview
More details of TCP/IP Configuration plugin is available here
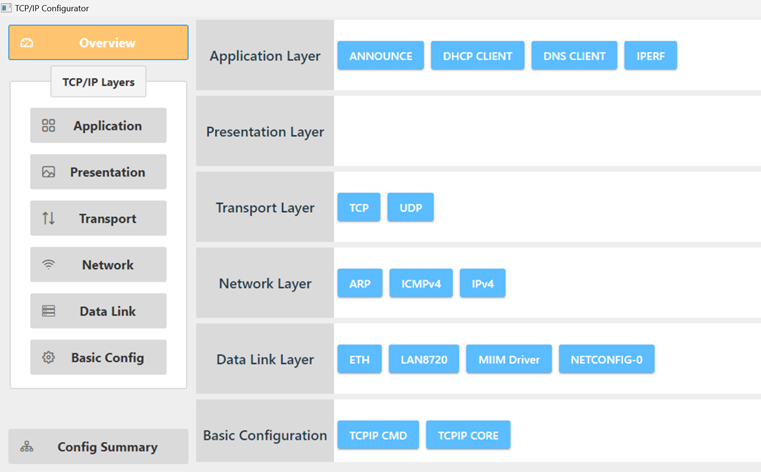
The Application Layer modules enabled in the demo are as follows:
- Application Layer Modules
- ANNOUNCE to discover the Microchip devices within a local network.
- DHCP Client to discover the IPv4 address from the nearest DHCP Server.
- DNS Client provides DNS resolution capabilities to the stack.
- IPERF implements the iperf protocol to measure networking bandwidth and performance.
Downloading and Building the application
To clone or download this application from Github, go to the main page of this repository and then click Clone button to clone this repository or download as zip file.
This content can also be downloaded using content manager by following these instructions.
Path of the application within the repository is apps\iperf_demo\ .
To build the application, refer to the following list of demo configurations and open the project using MPLAB X IDE.
| Project Name | Target Device | Development Board | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| wbz653_curiosity.X | WBZ653 | WBZ653 Curiosity Board | TCP/IP IPERF Application - Bare Metal |
Hardware Setup - WBZ653 Curiosity
The target board for running the application is WBZ653 Curiosity.
This section provides essential hardware configuration of this target board to run TCP/IP applications.
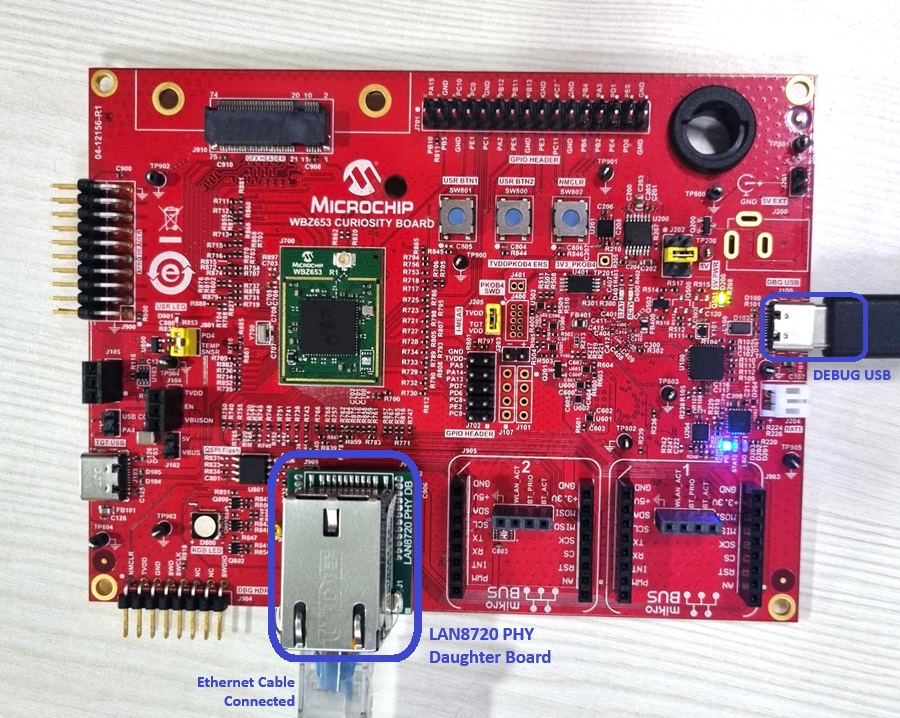
Board Setup
- Default jumper setting of the board is shown above.
- Connect the USB Type-C cable between DEBUG USB port on the board and host PC.
- Establish a connection between the router/switch with the WBZ653 Curiosity board through the RJ45 connector, using the Ethernet cable.
Running the Application
- Open a terminal application on the host computer (like Hyper-terminal or Tera Term).
- Configure the terminal application for serial port “USB Serial Device”.
- Set baud rate as 115200 in the terminal application.
- Build and download the application project on the target board.
- Verify the TCP/IP Stack initialization console messages.
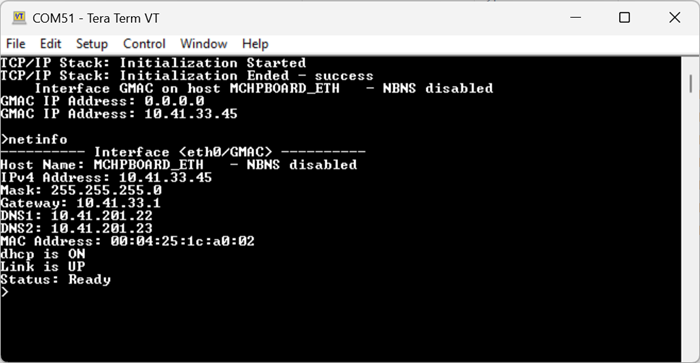
If DHCP client is enabled in the demonstration, wait for the DHCP server to assign an IP address for the development board.
This will be printed on the console. Otherwise, the default static IP address will be assigned to the board.
By entering the command netinfo, the response is obtained as shown above.
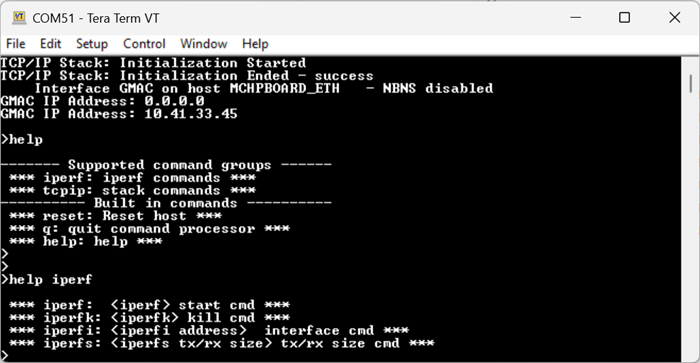
By entering the command help iperf , the response is obtained as shown above.
Iperf Test
To run Iperf test, the host computer must have an Iperf utility installed.
A brief description of the commands for Iperf application is as follows:
- iperf: starts the iperf session. Use "iperf -s" for a server connection or "iperf -c <address>" for a client connection. See the Iperf module documentation and Network Metrics for the command syntax & throughput measurements.
- iperfk: kills an ongoing iperf test. This is mainly useful for killing a iperf server waiting for connections. But the command could be also used to abort client test.
- iperfi: to set the interface to use for iperf when the test is run on a multi-interface host. When multiple iperf instances are used, the extra parameter "-i" should be used to specify the iperf index to which the command refers to.
- iperfs: to set the socket TX or RX buffer size dynamically. For example: iperfs -tx 2048
Note:
- While running iperf demo, enable only required TCP/IP modules. This will give better throughput by minimizing the software stack overhead.
- The data throughput could vary dependent on the iperf socket settings and the network conditions.
- Larger TX and RX buffers will increase the throughput.
- Connect the board, running the iperf demo, directly to the host computer to avoid other network nodes affecting the throughput results.
