3.1.2 MCC Melody Components
The Libraries, Drivers and Hardware peripherals, which make up MCC Melody, are collectively referred to as components. Libraries and Drivers are not directly dependent on any microcontroller (MCU) hardware, relying on PLIBs (Peripheral Libraries), which provide the hardware abstraction. The following figure illustrates MCC Melody’s structure.
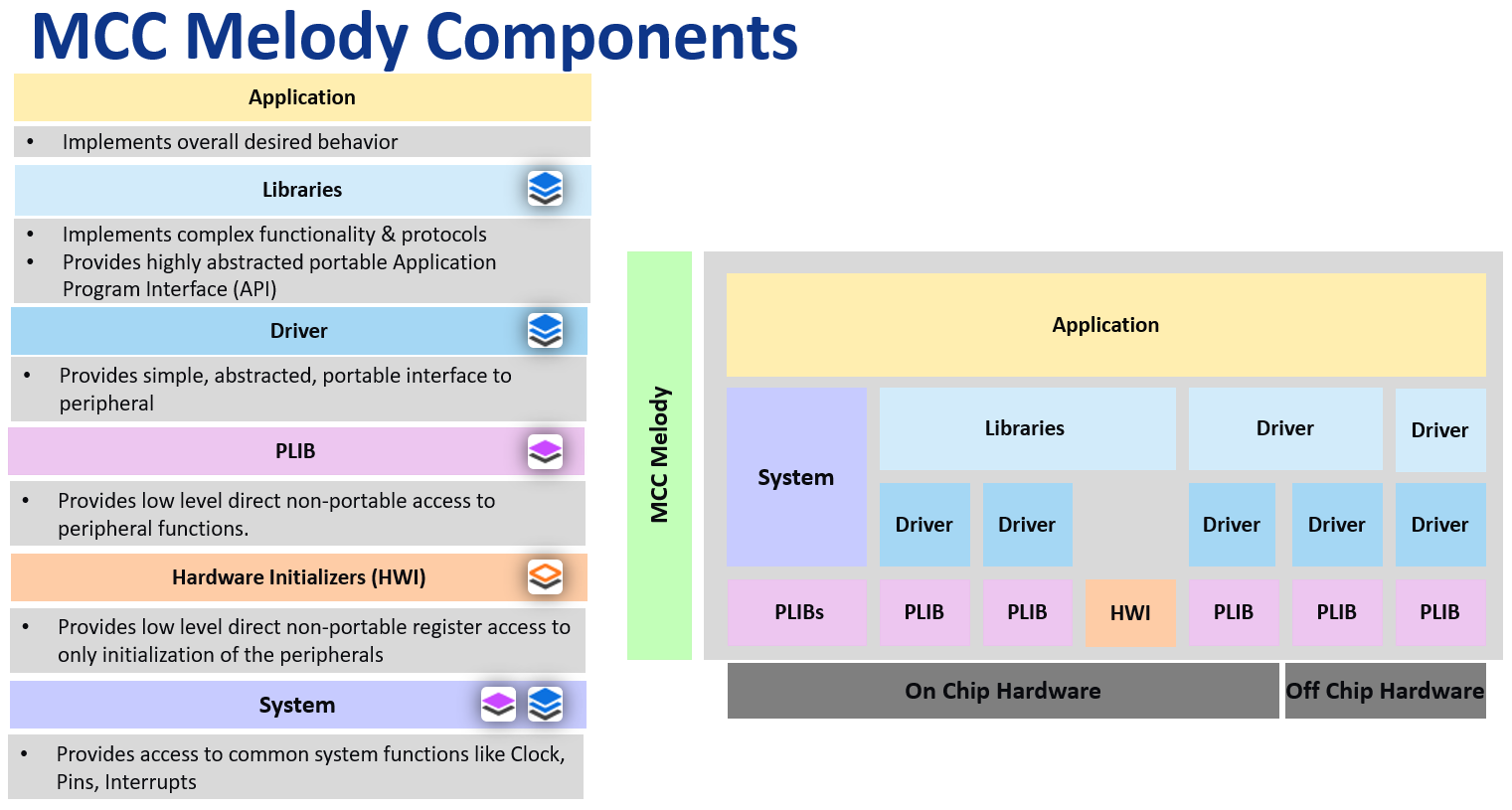
The MCC melody components show in Device- and Project-Resources as follows. Icons indicate the degree of separation from the microcontroller hardware, presented as the black layer at the bottom. The more layers, the more independent the component is from the microcontroller’s hardware.
Hardware independence facilitates portability in the following ways:
- Configuration portability: A use-case-focused configuration interface gives the ability to select/easily change a component's underlying hardware dependency.
- Firmware portability: Writing application code using portable interface API ensures that it's easy to change a peripheral instance the code runs on.
| Component Category | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Libraries provide one of the following:
|
 |
 |
Drivers support both Configuration and Firmware portability, providing an easy-to-read and efficient abstraction to the functionality of the peripheral, for example, UART, I2C Host, I2C Client, and so on. |
 |
 |
Peripheral Libraries (PLIB) may provide firmware portability, but in general, only a non-portable interface to peripheral functionality |
 |
 |
Hardware Peripherals (Initializers) provide non-portable direct access to peripherals and their registers. As the name suggests, only an initialization function is generated. |


