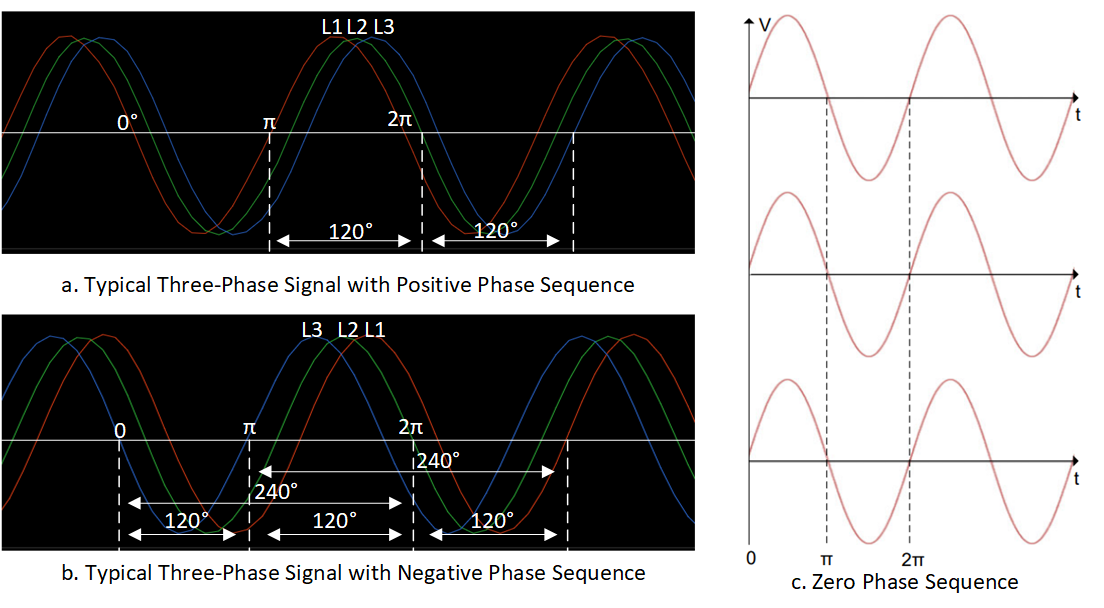
2.1 Three-Phase Power Supply
A three-phase power supply system is the most common method of electric power generation, transmission, distribution and consumption worldwide.
The three-phase power comprises three alternating phases, generally represented as L1, L2 and L3. All three phases produce A/C voltages of equal amplitude and frequency with reference to ground potential. All three-phase voltages are phase shifted to each other by 120°, as shown in Figure 2-1a.