1.3 FAT Filesystem throughput using SDMMC Media
This application calculates throughput by Writing and Reading data into a SD-Card at High Speed using the MPLAB Harmony File System and the SDMMC driver.
Description
Application performs below filesystem operations and throughput calculations on SD-Card using both Aligned and Unaligned buffers
- Opens a file named throughput.txt in the root directory of the SD card
- Writes 10 Megabytes of data to file in chunks of 64 Kilobytes
- Once the operation is completed it calculates the time taken and overall throughput for write in Megabytes/second and displays on the console
- Reads 10 Megabytes of data from file in chunks of 64 Kilobytes
- Once the operation is completed it calculates the time taken and overall throughput for reading in Megabytes/second and displays on the console
- Closes the file once read is completed
- Checks if the Above steps need to be repeated for Unaligned buffer. If already done then it Glows an LED reporting success and the console will have throughput information for both Aligned and Unaligned buffers.
File system layer uses:
- SDMMC Driver to communicate to SD Card
Downloading and Building the Application
To clone or download this application from Github, go to the main page of this repository and then click Clone button to clone this repository or download as zip file. This content can also be downloaded using content manager by following these instructions.
Path of the application within the repository is apps/fs/sdmmc_fat_throughput/firmware.
To build the application, refer to the following table and open the project using its IDE.
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pic32mz_das_sk.X | MPLABX project for PIC32MZ Embedded Graphics with Stacked DRAM (DA) Starter Kit (Crypto) |
Setting Up the Hardware
The following table shows the target hardware for the application projects.
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pic32mz_das_sk.X | PIC32MZ Embedded Graphics with Stacked DRAM (DA) Starter Kit (Crypto) |
- To run the demo, the following additional hardware are required:
- One micro-sd card
- The SD Card should have at least 10MB of free space for the demo to work
- One micro-sd card
Setting Up PIC32MZ Embedded Graphics with Stacked DRAM (DA) Starter Kit (Crypto)
- Connect the Debug USB port on the board to the computer using a micro USB cable
- Connect a micro USB cable to the USART-USB port J5
Running the Application
- Open the Terminal application (Ex.:Tera term) on the computer
- Connect to the “USB to UART” COM port and configure the serial settings as
follows:
- Baud : 115200
- Data : 8 Bits
- Parity : None
- Stop : 1 Bit
- Flow Control : None
-
Build and program the application using its IDE
-
Following message is output on console:
- Insert the SD Card in the SD Card slot of the Device
-
The LED is turned ON if there was no error during the file operations
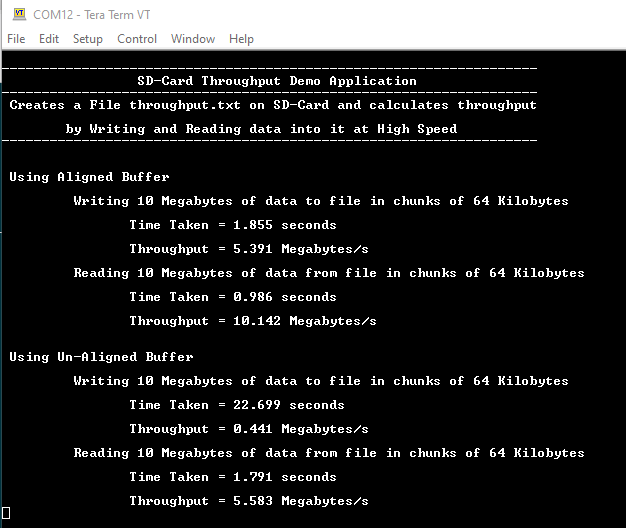
Refer to the following table for LED name: - Calculated throughput values for Aligned and Un-aligned buffers are displayed on
console as below:
- Note: The Values showed in the below output may differ slightly when demo is run
Additional Steps (Optional)
To increase the throughput for the Un-aligned buffers you can follow below steps
- Update the app.c file to place the application buffer in non cacheable space using __COHERENT attribute or CACHE_ALIGN macro as below uint8_t CACHE_ALIGN __ALIGNED(CACHE_LINE_SIZE) dataBuffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
OR
- Launch MCC for the project
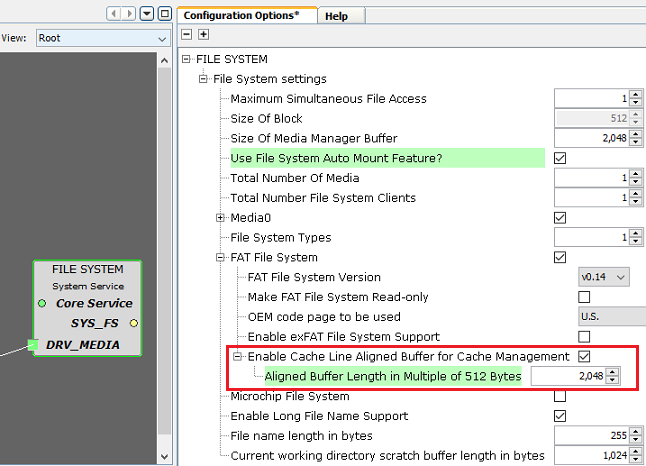
- Increase the size for the internal aligned buffer used by Filesystem service
with some value as shown below. This internal buffer will be used when
application buffer is Un-aligned and placed in cacheable region.
- Note: Increasing the size of the aligned buffer will consume
more RAM
- Note: Increasing the size of the aligned buffer will consume
more RAM
- Regenerate the project
- Once done repeat the steps mentioned in Running The Application and observe the change in throughput for Un-aligned buffer
