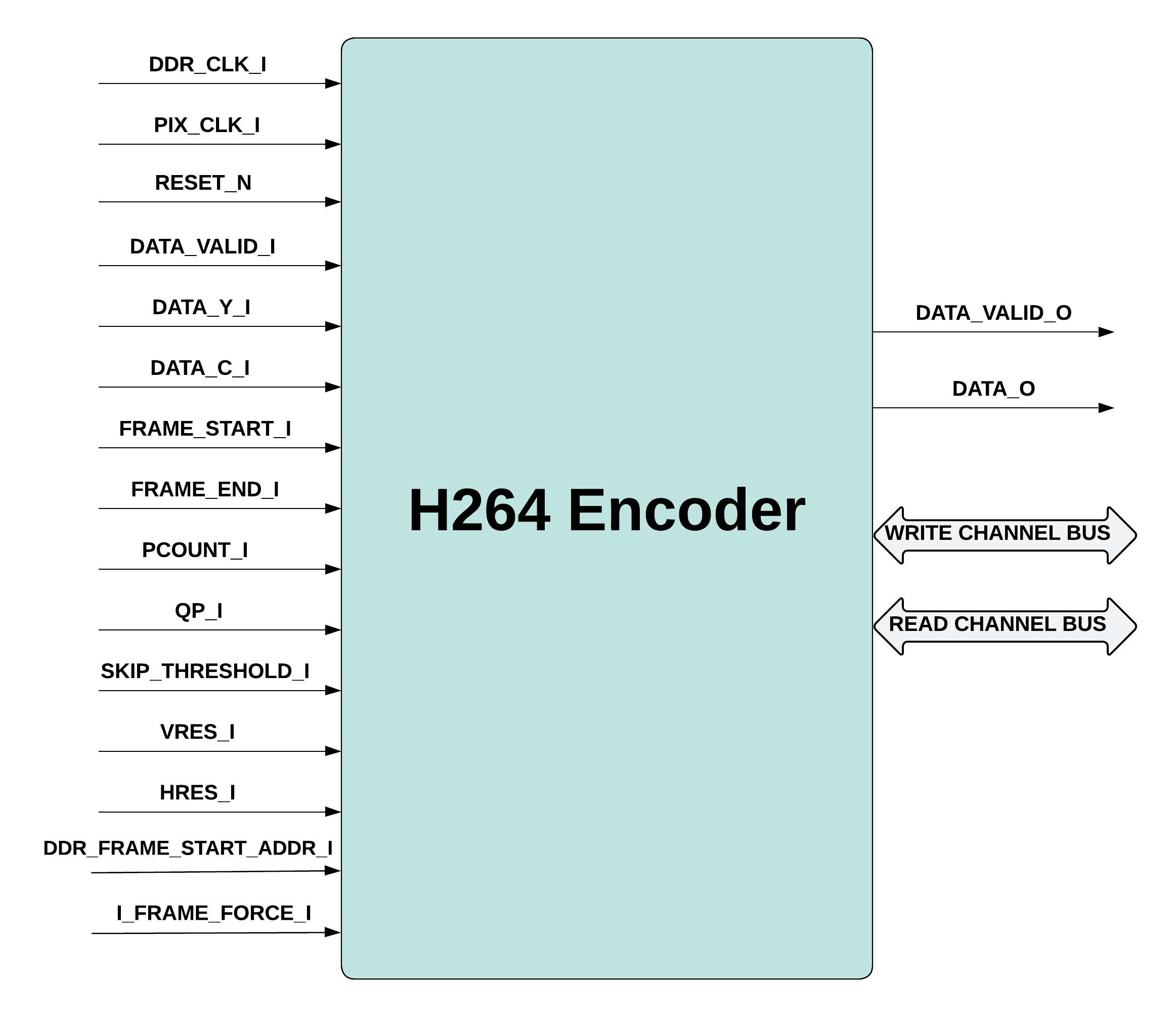
Introduction
H.264 is a popular video compression standard for compression of digital video. It is also known as MPEG-4 Part10 or Advanced Video Coding (MPEG-4 AVC). H.264 uses block-wise approach for compressing the video where the block size is defined as 16 x 16 and is called a macro block. The compression standard supports various profiles that define the compression ratio and complexity of the implementation. The video frames, to be compressed, are treated as I frame, P frame, and B frame. An I frame is an intra-coded frame where compression is done by using the information contained within the frame. No other frames are required to decode an I frame. A P frame is compressed by using the changes with respect to an earlier frame that can be an I frame or a P frame. The compression of B frame is done by using the motion changes with respect to both an earlier frame and an upcoming frame.
The I and P frame compression process has four stages:
- Intra/Inter prediction
- Integer transformation
- Quantization
- Entropy encoding
H.264 supports two types of encoding:
- Context Adaptive Variable Length Coding (CAVLC)
- Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC)
The current version of H.264 Encoder implements baseline profile and uses CAVLC for entropy encoding. Also, H.264 Encoder supports encoding of I and P frames.