2 Period Jitter
Although the official definition of period jitter is the difference between a measured clock period and the ideal period, in real world applications it is often difficult to quantify the ideal period. If we observe the output from an oscillator set to 125MHz using an oscilloscope, the average measured clock period may be 7.996ns instead of 8ns. Therefore, it is more practical to treat the average observed period as the ideal period and this a common practice by timing device manufacturers. The standard procedure for measuring period jitter involves randomly measuring the duration of one clock period 10,000 times and using the recorded data to calculate the mean, standard deviation, and peak-to-peak values. Due to the random nature of period jitter, the peak-to-peak values can vary greatly and, often times, period jitter needs to be re-calculated several times to come up with an average value.
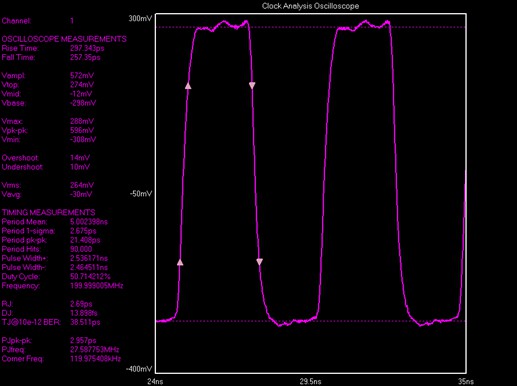
Below is an example of period jitter measured on a Wavecrest SIA-3300C signal integrity analyzer for a 200MHz XO. This analyzer platform is setup to measure 30,000 samples at a time and is executed three times in order to obtain an average peak-to-peak value.