10 Advanced Topics
Additional reading for advanced users.
10.1 Clocking the Configurable Logic Block
How the CLB relates to clocks.
The CLB peripheral receives clock input from the source specified in the CLK field in the CLBCLK register, written from the CPU. Consult the data sheet for available clock sources.
The CLB also includes a clock divider, which must be configured along with the logic design and incorporated into the bit stream. The clock source can be divided by 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 or 128.
The CLB clock is distributed to all BLE flip-flops, so the logic design runs off the same clock. Although logic design schematics can include various flip-flop types, it is impossible to connect or configure an individual clock source.
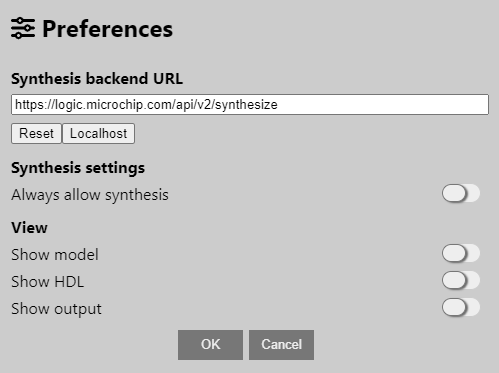
10.2 Preferences
The preferences panel is accessed via the main drawer menu.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Synthesis backend URL | The synthesis server URL must not be changed unless instructed to by Microchip support engineer |
| Always allow synthesis | Used to bypass Design checker errors by graying out the Synthesize button |
| Show model | The right-hand pane will show the “GUI model” of the current design—this is for internal debugging of the GUI |
| Show HDL | The right-hand pane will show the intermediate HDL of the current design. This content will be sent to the backend for synthesis, for internal debugging of the interface between the GUI and backend |
| Show output | The right-hand pane will show output from the synthesis engine—this is for internal debugging of the backend logic-synthesis engine |
10.3 Making Use of the Output ZIP
How to use the output.
The synthesis process always returns a ZIP file with outputs.
The ZIP file is intended for the CLB Synthesizer Web version's users who want to convert a logic design into a bit stream.
- The resultant bit stream
- A basic CLB driver for configuring the peripheral
- Build artifacts
Refer to the readme inside the ZIP for further details.
10.4 Description of Output Files
After synthesis, a ZIP file containing many build artifacts can be downloaded.
- Root folder: Outputs for use in bare metal projects
- Build folder: Debug artifacts from the build process
- Input folder: Inputs passed into the server for processing
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
readme.txt | Instructions for bare metal users |
clb1.c; clb1.h | Driver for configuring and enabling the CLB |
clb1_output_mappings.h | Header file defining output mappings from the CLB to peripherals |
bitstream.s | Bit stream in assembler format for embedding into a bare metal project |
pre-routing.svg | Diagrammatic representation output from Yosys (generic) |
routed.svg | Diagrammatic representation post-routing |
build/bitstream.json | Bit stream words in JSON format |
build/out.fasm | Output from FASM stage |
build/out.net | Pre-routing acked netlist in XML format |
build/out.net.post_routing | Post-routing packed netlist in XML format |
build/out.netlist | Binary form of netlist |
build/out.phys | Binary form of physical netlist |
build/out.place | Placer output report |
build/out.route | Router output report |
build/packaging_pin_util.rpt | Packing pin usage report |
build/pre-routing.dot | Input to pre-routing SVG |
build/pre-routing.v | Verilog netlist output from Yosys (before place and route) |
build/routed.dot | Input to post-routing SVG |
build/routed.v | Bels format netlist post-routing |
build/stderr.txt | Backend stderr log |
build/stdout.txt | Backend stdout log |
build/vpr_stdout.log | Place and route output |
build/yosys.log | Log from Yosys synthesis stage |
build/synth.json | JSON formatted netlist output from Yosys |
input/*.v | Verilog representation of input design |
input/*.xdc | Mappings to physical pins |
input/project.json | Top-level description of the design |
input/stats.json | Statistical summary of the design |
input/*.clb | Save-file for the design |
10.5 Synthesis and Place-and-Route Process
What happens behind the scenes?
Once an application has been captured in the CLB Synthesizer GUI, it needs to be converted into a configuration bit stream, which can be loaded into the CLB module. This process is known as “synthesis”, although it also includes place and route steps and is done by Microchip’s online web service.
It is unnecessary for the user to understand how this process works—a brief summary is given here for advanced or curious users.
How It Works
- The CLB application schematic drawings are converted to equivalent Verilog descriptions and sent to the backend for processing.
- The first stage in the backend process is logic synthesis. Logic synthesis is a process to convert the Verilog textual representation of a logic design into a netlist, which describes the hardware in equivalent logic gates and wires. Logic synthesis is done using Yosys Open SYnthesis Suite, which is equipped with a plug-in describing the actual structure of the logic elements in the CLB module. The output of the synthesis stage is a Verilog netlist.
- The next stage is Place-and-Route (PnR). During this stage, the netlist elements are mapped into physical locations in the CLB array (placement), and interconnects are made between them (routing), which is a complex and iterative process and is not ensured to achieve an outcome (e.g., if exceeding space or routing constraints). PnR is done using the VPR provided by Verilog to Routing (VTR), which is equipped with a plug-in that describes the available interconnects within the CLB module. The output of the PnR stage is a FASM file, which specifies the CLB configuration content in a generic, plain-text format.
- The final stage is bit stream generation. The bit stream generator parses the FASM file and converts the configuration of generic configurable logic resources into bit patterns in a bit stream according to the actual CLB bit stream implementation. The bit stream generator is a script specific to the Microchip CLB implementation. The output of the bit stream generator is a sequence of bits to be loaded into the CLB during configuration, which embeds as a sequence of data words (DW) stored as constants in Flash by the compiler during application building.
