6.1 Dedicated Spare or Auto-Replace Spare?
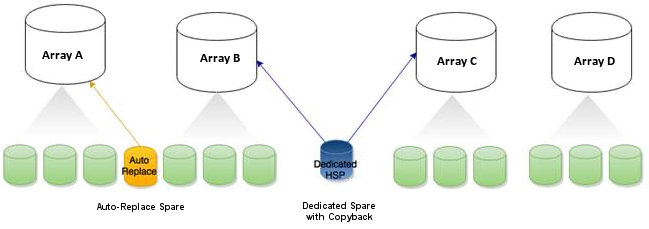
A dedicated hot spare is assigned to one or more arrays. It will protect any redundant logical drive on those arrays.
After using a dedicated hot spare to rebuild a failed logical drive, data is moved back to its original location, using a process called copyback, once the controller detects that the failed drive has been replaced. Once the data is copied back, the hot spare becomes available again. You must create an array before you can assign a dedicated hot spare to protect it. To assign a dedicated hot spare, see 6.3 Assigning a Dedicated Hot Spare.
An auto-replace hot spare is assigned to a specific array. It will protect any redundant logical drive on that array. After using an auto-replace spare to rebuild a failed logical drive, it becomes a permanent part of the array. You must create an array before you can assign an auto-replace hot spare to protect it. To assign an auto-replace hot spare, see 6.4 Assigning an Auto-Replace Hot Spare.