5.4 Cyclic Redundancy Check
In these methods the bootloader uses a CRC signature for application validation. To learn
more about the steps for the CRC verification of memory, refer to this reference.
Overview
In the CRC16 & CRC32 verification methods, a CRC signature is calculated over the application space. That value is compared to a pre-calculated CRC value stored at the end of the application hex file. If the calculated signature matches the signature stored in the application header, the application is allowed to launch. This form of verification is decent at detecting errors in communication and if the memory has been accidentally erased/overwritten. A CRC verification is not nearly as fast as a checksum, but provides better protection. CRC is also faster at validation than a hashing algorithm, but less secure in terms of memory protection due to the lack of authenticity checks.
Algorithms Used
CRC16-CCITT
| CRC Value | Hex |
|---|---|
| Seed | 0xFFFF |
| Polynomial | 0x1021 |
| XOR | N/A |
CRC32-JAM
| CRC Value | Hex |
|---|---|
| Seed | 0xFFFFFFFF |
| Polynomial | 0xEDB88320 |
| XOR | 0x00000000 |
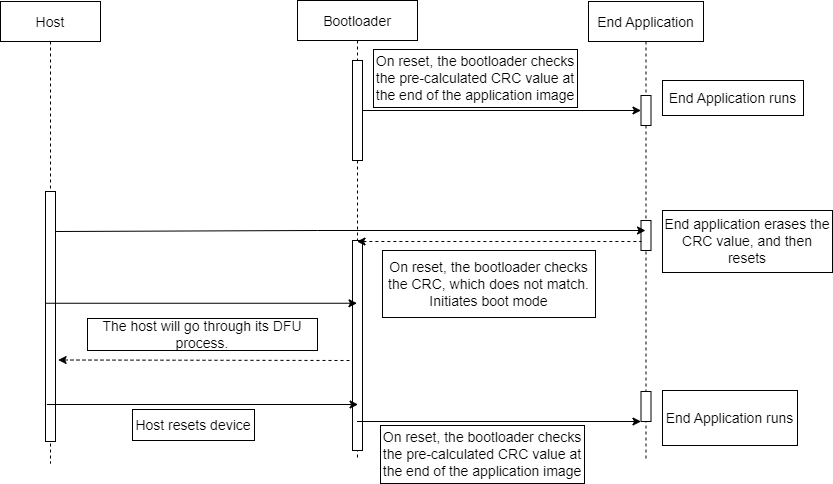
Verification Flow
In CRC16 and CRC32 verification, the bootloader has a very similar program flow to Checksum verification. The only difference is the type of hash that is used in the calculation.