2 Boot Time Optimization
Boot time optimization is an area of interest for most of the real-time systems and is an important component of system performance as users must wait for the boot to complete before they can use the device. Boot time optimization reduces the boot time of a system at various levels of booting.
This white paper provides a reference for measuring boot time benchmarking on the PolarFire SoC Icicle kit. It mainly focuses on HSS boot time, U-Boot time, Linux boot time, and System Services.
The following figure shows the Linux boot time parameters on PolarFire SoC Icicle kit.
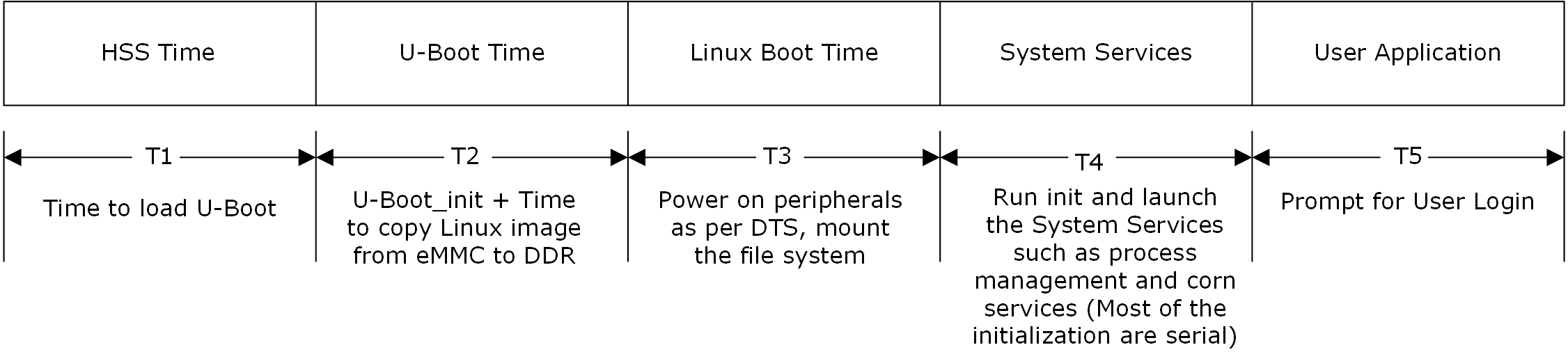
Kernel optimizations are considered at T1, T2, T3, and T4, as shown in the preceding figure.
The following table lists the software and hardware requirements for boot time optimization.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Yocto | 2020.12 |
| Buildroot | 2020.12 |
| Kernel | 5.6.16 |
| HSS | 2020.12 |
| U-Boot | 2020.12 |
| Hardware | Version |
| PolarFire SoC Icicle Kit | (MPFS250T_ES-FCVG484E) |
The area of optimizations are:
HSS Time: The time taken from the system start-up (searching the source for the payload and unpack) to the destination, that is, loading U-Boot from SD Card/eMMC to DDR. In this optimization, the search time for the source is reduced to one sec (which in general takes five seconds). Microchip banner is removed to reduce the overall booting time of the cores associated with the payload.
U-Boot Time: The time taken for the U-Boot initialization and copying the Linux image from the eMMC/SD Card to the DDR. U-Boot initializes the hardware minimally, which also locates, loads, and executes the kernel image. In this optimization, disabled features which have a significant impact, such as hardware probing features, device initialization, Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) reduces the boot time.
Linux Boot Time: The time taken to power-up peripherals, mounting the file systems, executing and launching the system services. Linux boot time includes kernel execution and system services boot time. In this optimization, removing console messages by adding quiet to the cmd line, eliminating printk to CONFIG_PRINTK, sizing down the device tree by removing the unsupported features and unnecessary hardware interfaces reduce the boot time.
Reducing the kernel size helps the kernel load faster. Obtaining a smaller kernel by eliminating the Kernel options such as CONFIG_IKCONFIG, CONFIG_HOTPLUG, CONFIG_KALLSYMS, CONFIG_DEBUG_KERNEL, CONFIG_IKCONFIG, CONFIG_DNOTIFY, CONFIG_INOTIFY, and CONFIG_AUTOFS4_FS (automounter), which are not necessary for Linux boot up, speeds up kernel loading, therefore, reducing the kernel initial time when the kernel is loaded.
