5.1.2.2 BLE Legacy Advertisements
This section explains how to enable BLE Advertisements on the PIC32-BZ6 Curiosity board using the MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC). In this basic application example, the advertisement interval will be set to 1 sec.
Users can choose to either run the precompiled Application Example hex file provided on the PIC32-BZ6 Curiosity Board or follow the steps to develop the application from scratch.
These examples build upon one another. It is recommended to follow the examples in sequence to understand the basic concepts before progressing to the advanced topics.
Recommended Readings
-
Getting Started with Application Building Blocks – See Building Block Examples from Related Links.
-
Getting Started with Peripheral Building Blocks – See Peripheral Devices from Related Links.
-
FreeRTOS and BLE Stack Setup – See Peripheral - FreeRTOS BLE Stack and App Initialize from Related Links.
-
BLE Software Specification – See MPLAB® Harmony Wireless BLE in Reference Documentation from Related Links.
Hardware Required
| S. No. | Tool | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PIC32-BZ6 Curiosity Board | 1 |
| 2 | Micro USB cable | 1 |
| 3 | Android/iOS Smartphone | 1 |
| 4 | (Optional) Power
Debugger(1)/Multimeter/Oscilloscope to measure power
Note:
| 1 |
SDK Setup
Refer to Getting Started with Software Development from Related Links.
Software
To install Tera Term tool, refer to the Tera Term web page in Reference Documentation from Related Links.
Smartphone App
Light Blue iOS/Android app available in stores.
Programming the Precompiled Hex File or Application Example
Using MPLAB® X IPE:
- Import and program the
precompiled hex file:
<Harmony Content Path>\wireless_apps_pic32_bz6.\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\legacy_adv\precompiled_hex\legacy_adv.X.production.signed.hex - For detailed steps, refer to
Programming a Device in MPLAB® IPE in
Reference Documentation from Related Links.Note: Ensure to choose the correct Device and Tool information.
Using MPLAB® X IDE:
- Perform the following the steps mentioned in Running a Precompiled Example. For more information, refer to Running a Precompiled Application Example from Related Links.
- Open and program the application:
<Harmony Content Path>\wireless_apps_pic32_bz6
\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\legacy_adv\firmware\legacy_adv.X. - For more details on how to find the Harmony Content Path, refer to Installing the MCC Plugin from Related Links.
Demo Description
This application example enables transmitting non-connectable, undirected BLE Advertisements. On reset, “Advertising” will appear on a terminal emulator like TeraTerm, denoting the start of advertisements.
Testing
- Using a micro USB cable, connect the Debug USB on the Curiosity board to a PC.
- Program the precompiled hex file or application example as mentioned.
- Open Tera Term:
- Set the “Serial Port” to USB Serial Device.
- Speed to 115200.
- Press the NMCLR Button on the
Curiosity board and console should output this.
- Open the LightBlue app on
your smartphone to scan for advertisements. A device with the name
“pic32cx-bz6” will appear. Users with an iOS device may see the device name
as “Microchip”.
- Users using a wireshark
sniffer can examine the complete Application Payload sent.
Figure 5-71. Wireshark 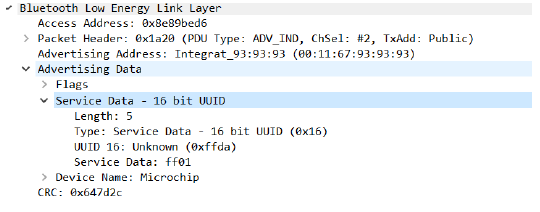
Current Consumption Measurement
Hardware modification
Remove the resistors R925 and R777 on PIC32-BZ6 Curiosity board .
Developing this Application from scratch using MPLAB Code Configurator
-
Create a new harmony project. For more details, see Creating a New MCC Harmony Project from Related Links.
- Setup the basic components and
configuration required to develop this application, import component
configuration:
<Harmony Content Path>\wireless_apps_pic32_bz6\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\legacy_adv\firmware\legacy_adv.X\legacy_adv.mc3. - Accept dependencies or satisfiers when prompted.
- Verify if the Project Graph
window has all the expected configuration.
Figure 5-72. Project Graph
Verify Advertisement Configuration
- Select the BLE Stack component in the Project Graph.
- Configure Extended Advertisements in the Configuration Options panel as shown in the following image.
Generating Code
For more details on code generation, refer to MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC) Code Generation from Related Links.
Files and Routines Automatically Generated by the MCC
After generating the program source from the MCC interface (by clicking Generate Code), the BLE configuration source and header files can then be found in the following project directories.
Initialization routines for OSAL, RF System, and BLE System are auto-generated by the
MCC. See OSAL Libraries Help in Reference Documentation from Related
Links. Initialization routine executed during program initialization can be found in
the project file.C.
initialization.cThe BLE stack initialization routine executed during Application Initialization can be found in project files. This initialization routine is automatically generated by the MCC. This call initializes and configures the GAP, GATT, SMP, L2CAP and BLE middleware layers.
app_ble.cAutogenerated, Advertisement Data Format
| Source Files | Usage |
|---|---|
app.c | Application State machine, includes calls for Initialization of all BLE stack (GAP,GATT, SMP, L2CAP) related component configurations |
app_ble.c | Source code for the BLE stack related component configurations,
code related to function calls from app.c |
app_ble_handler.c | GAP, GATT, SMP and L2CAP event handlers |
app.c is autogenerated and has a state machine-based application
code sample. Users can use this template to develop their own application.Header Files
ble_gap.hcontains BLE GAP functions and is automatically included inapp.c
Function Calls
- MCC generates and adds the code
to initialize the BLE Stack GAP, GATT, SMP and L2CAP in
APP_BleStackInit() APP_BleStackInit()API is called in the Applications Initial StateAPP_STATE_INITinapp.c
User Application Development
Include
- Include the user action. For more information, refer to User Action from Related Links.
definitions.hmust be included in all the files, where UART will be used to print debug information.Note:definitions.his not specific to UART but instead must be included in all the application source files where any peripheral functionality will be exercised.
Set Public Device Address in app_ble.c.
BLE_GAP_SetDeviceAddr(&devAddr);
BLE_GAP_Addr_T devAddr;
devAddr.addrType = BLE _GAP_ADDR_TYPE_PUBLIC;
devAddr.addr[0] = 0xA1;
devAddr.addr[1] = 0xA2;
devAddr.addr[2] = 0xA3;
devAddr.addr[3] = 0xA4;
devAddr.addr[4] = 0xA5;
devAddr.addr[5] = 0xA6;
// Configure device address
BLE_GAP_SetDeviceAddr(&devAddr);app_ble.capp.c.BLE_GAP_SetAdvEnable(0x01, 0x00);APP_STATE_INIT in app.capp.cWhere to Go from Here
See BLE Connection from Related Links.
