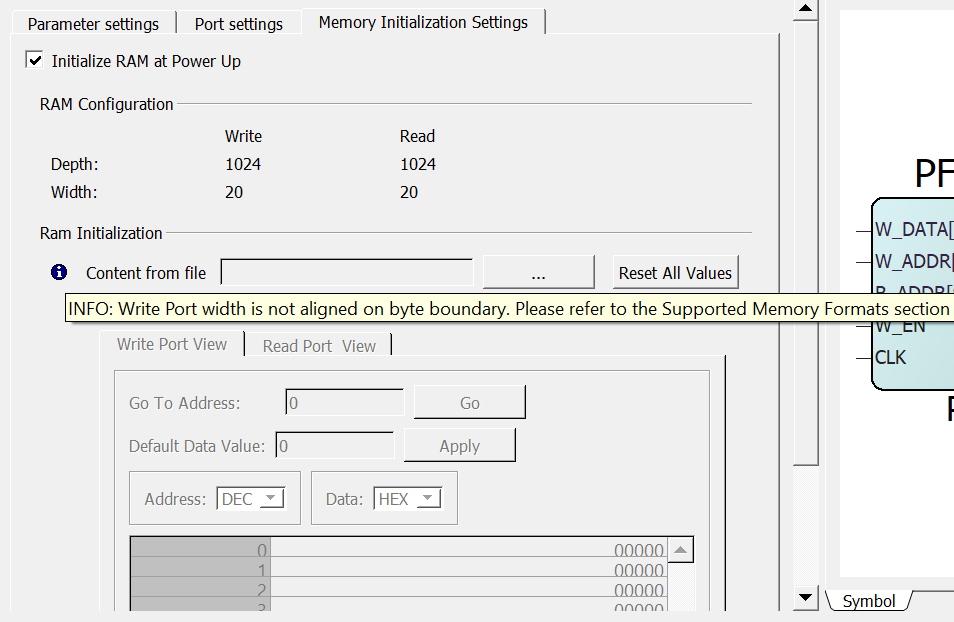
4.1.3.2 4-Bit Write Port Width
(Ask a Question)Enter a short description of your concept here (optional).
Consider the following Intel HEX memory file.
The binary stream of bits for above memory file data is:
The following figure shows the equivalent memory file data padded with zeros to achieve a 4-bit write port width.
When the tool parses the above memory file data (padded with zeros), it converts the data to binary and reads it as a stream of bits. If the port width is 4 bits, the tool reads 8 bits (byte-aligned), ignores the upper 4 bits of actual data, and stores the lower 4 bits of actual data in RAM, as listed in the following table.
| Address | Data |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0xF |
| 1 | 0xF |
| 2 | 0x1 |
| 3 | 0x1 |
| 4 | 0xE |
| 5 | 0xE |
| 6 | 0x2 |
| 7 | 0x2 |
| 8 | 0xD |
| 9 | 0xD |
| A | 0x3 |
| B | 0x3 |
| C | 0xC |
| D | 0xC |
| E | 0x4 |
| F | 0x4 |
| 10 | 0xB |
| 11 | 0xB |
| 12 | 0x5 |
| 13 | 0x5 |
| 14 | 0x0 |
| 15 | 0x0 |
| 16 | 0x2 |
| 17 | 0x1 |