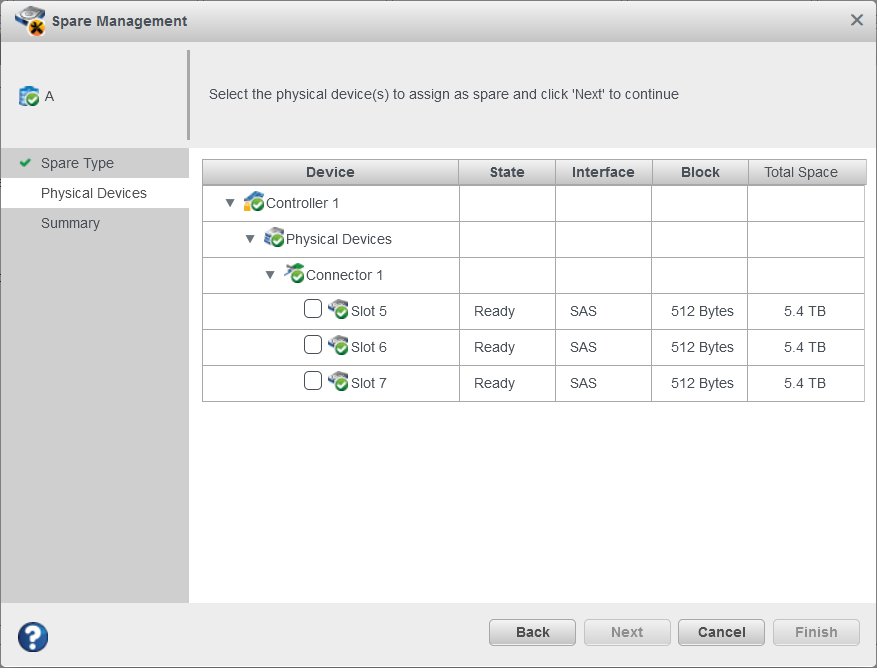
10.7 Assigning Spares at the Array Level
Dedicated and auto-replace spare for SED logical device can be assigned at the array level.
Assigning a dedicated/auto-replace spare for an encrypted array: Only the self-encrypting drive of the same SED type is allowed to assign a spare, for example; if an array is created with SED type enterprise, then only the enterprise drive is allowed to assign a spare.
Once the encrypted array is assigned with a dedicated spare, the dedicated spare drive can only protect encrypted arrays, which is created using same SED type drives. Similarly, once the plaintext/unsecured array is assigned with a dedicated spare, that dedicated spare drive can only protect plaintext/unsecured arrays which is created using same SED type drives.
Assigning a dedicated spare for a plaintext/unsecured array (SED drives): Only the self-encrypting drive of the same SED type is allowed to assign a spare. For example, if an array is created with SED type Enterprise, then only the enterprise drive is allowed to assign a spare. Later, the array cannot be converted to an encrypted data as a dedicated spare (Sharable Spare) is assigned.
Assigning an auto-replace spare for a plaintext/unsecured array (SED drives): Only the self-encrypting drive of same SED type is allowed to assign a spare. For example, if an array is created with SED type Enterprise, then only the enterprise drive is allowed to assign a spare. And once auto-replace spare is assigned, it can convert the plaintext/unsecured data to the encrypted data.
While selecting the array that is created using self-encrypting drive, the Spare Management window only lists the valid self-encrypting drive for the spare assignment.