1.3 ROM Code Valid Boot Code Pattern
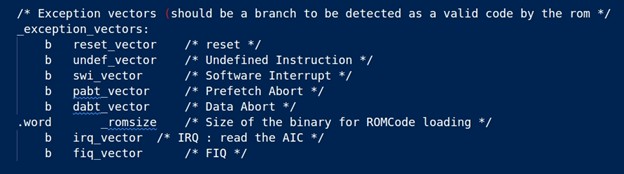
The ROM code reads and analyzes the first 28 bytes, corresponding to the first seven vectors of the second-stage bootloader (at91bootstrap in this case), to determine whether it can be considered as a valid boot code pattern or should be skipped.
All exception vectors, including the sixth vector, must use Arm instructions to either branch or load the PC (program counter register) with PC-relative addressing.
The sixth exception vector is used by the ROM code to assess the size of the at91bootstrap image, and thus determine the number of bytes to be transferred from the external non-volatile memory into the first half of the internal SRAM0.
If the external NVM chosen is an SD/e.MMC card with FAT32 partitions, the ROM code looks for a boot.bin file instead of reading raw data from the non-volatile memory. It then searches for the required boot pattern in the first 28 bytes of the data.
The at91bootstrap code ensures the presence of valid code by providing the proper exception vector table. This can be seen in crt0_gnu.s in the at91bootstrap source code.