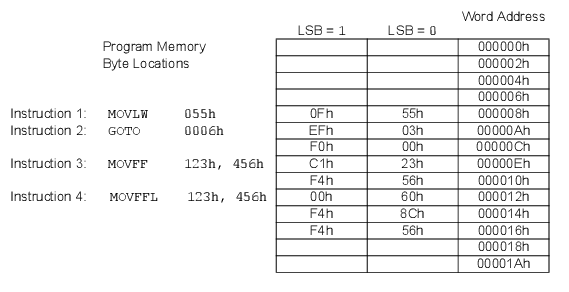
7.4.2 Instructions in Program Memory
The program memory is addressed in bytes. Instructions are stored as
either two bytes, four bytes, or six bytes in program memory. The Least Significant Byte of
an instruction word is always stored in a program memory location with an even address (LSb
= 0). To maintain alignment with instruction boundaries, the PC increments
in steps of two and the LSb will always read ‘0’. See the “Program
Counter” section in the “Memory Organization” chapter for more details. The
instructions in the Program Memory figure below shows how instruction words are stored in
the program memory.
The CALL and GOTO instructions have the absolute program memory
address embedded into the instruction. Since instructions are always stored on word
boundaries, the data contained in the instruction is a word address. The word address is
written to the corresponding bits of the Program Counter register, which accesses the
desired byte address in program memory. Instruction #2 in the example shows how the
instruction GOTO 0006h is encoded in the program
memory. Program branch instructions, which encode a relative address offset, operate in the
same manner. The offset value stored in a branch instruction represents the number of
single-word instructions by which the PC will be offset.