4.19 Power Over Ethernet BT (PoE) Configuration
The PoE Configuration page allows you to inspect and configure the current PoE port settings.
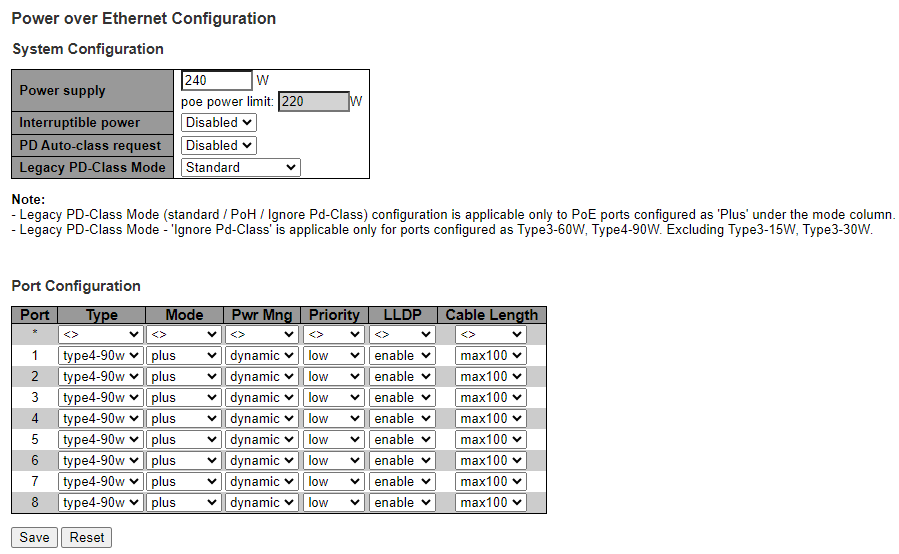
The PoE Configuration page has the following parameters:
- System Configuration
- Power Supply: For systems with an external power supply, the available power supply must be specified. For systems with a built-in power supply, the available power is shown. Values are in Watts.
- Interruptible power: Controls if PoE power should be interrupted (shutdown for 5 Sec) during unit software restart cycle, or remain unchanged during the unit software restart cycle.
- Disabled: PoE power remains unchanged during the entire unit software restart cycle
- Enabled: PoE power to already powered PD devices is turned off for 5sec during unit software restart cycle
- PD Auto-class request: is part of PoE IEEE 802.3bt in which the PD communicates its effective maximum power consumption to the PSE. The PoE port is to set its maximum allocated power in accordance with the maximum power consumed by the PD during the PD auto-class request negotiation cycle, instead the PD Class 0-8.
For example, a PD of type class-6 (60W) supporting PD Auto-Class request, may advertise through the PD Auto-Class request hardware handshake negotiation algorithm that it requires only 17W. As a result, the PoE limits port maximum power to 17W although the PD is from type class-6 (60W).
- Disabled: PoE maximum power is determined based on PD class regardless of the PD advertising that it supports PD Auto-class
- Enabled: PoE maximum power is determined based on the maximum power consumed by the PD during the PD auto-class request negotiation cycle
- Legacy PD-Class Mode: Legacy PD-Class Mode (standard/PoH/Ignore PD-Class) configuration is applicable only to PoE ports configured as Plus-Mode and is ignored for PoE ports configured as standard mode.
- Standard: Extend PD detection resistance/capacitance range beyond IEEE 802.3bt specification. Power-Demotion, which means that PD is allocated power from a PSE that is lower than what the PD requested, is supported.
- PoH: Same as Standard-Mode except for PoE-AT PDs advertising class 4, 4 (DSPD) or class 4 (SSPD). PoE-AT DSPD class 4, 4 will be offered 90W (instead of 60W). PoE-AT SSPD class 4 will be offered 45W (instead of 30W). No support for Power-Demotion.Note: A PoE-BT class 4,4 PD will be offered 60W, and PoE-BT SSPD class 4 will be 30W
- Ignore PD-Class:
- Port configured as Type4-90W is limited to 90W (DSPD) or 45W (SSPD) regardless of PD advertised class. No support for Power-Demotion.
- Port configured as Type3-60W is limited to 60W (DSPD) or 30W (SSPD) regardless of PD advertised class. No support for Power-Demotion.
- Port configured as Type3-30W/Type3-15W perform as if it’s configured in a Standard-Mode
- Port Configuration
- Port: Switch port number. Only PoE-capable ports are shown.
- Type: Configure the maximum power the PoE port can deliver to the PD before shutting it down. Power demotion is however supported, and therefore a lower power may in effect by provided. PoE Power demotion example: A PD advertises itself as class-8 90W, while the PoE port is either configured to Type3-60W offering up to class-6 60W, or due to limited free available power the PoE port is only allowed to offer up to class-6 60W. In either of these scenarios, the switch demotes the PD to class-6 60W. It’s up the PD to decide if to accept the 60W offer.
- Type4-90W: PoE maximum power is limited to 90W/45W (4-pair/2-pair)
- Type3-60W: PoE maximum power is limited to 60W/30W (4-pair/2-pair)
- Type3-30W: PoE maximum power is limited to 30W
- Type3-15W: PoE maximum power is limited to 15W
- Mode: Configure PoE port to one of the following options
- Disabled: PoE port is disabled. Port becomes a non-PoE switch Ethernet port
- Standard: PoE port is enabled and compliant with IEEE 802.3bt specification
- Plus: PoE port is enabled and supports non-IEEE-802.3-af/at/bt PoE PDs
- Power Management Mode: Configure the method used for calculating the free available power for additional PDs. Whenever PoE LLDP is enabled, PoE port max power is determined by remote PD Power-Request over LLDP regardless to Power Management mode
- Dynamic: Deduct from the free available power the actual PD power consumption, ignoring PD class
- Static: Use PD class to deduct from the free available power (SSPD class-8 = 90W, class-7= 75W, SSPD class-6 = 60W, and so on. DSPS class-5, 5 = 90W, DSPD class 4, 4 = 60W, etc.), considering power demotion, while ignoring actual PD power consumption. For PDs transmitting Power Over-MDI TLV in LLDP packet, free available power is deducted by the PD LLDP power-request value plus cable length power loss.
- Hybrid: Mixture of dynamic and static power management. Any PoE port configured as Hybrid will act as if it was configured to dynamic mode unless it has negotiated a maximum power consumption over LLDP. A port that negotiated a successful maximum PoE power over LLDP will be switched automatically to static mode limited to the negotiated power.
- Priority: PoE port priority controls the order of the PoE ports during Power-On sequence and during Power-Off sequence whenever overall power consumption exceeds the maximum available power. All ports configured as Critical are turned on first, followed by all ports configured as High, and lastly all ports configured as Low. For all ports of the same priority, the lowest PoE switch port number will be turned on first, followed by the next highest PoE switch port number. For example, if all ports are set to priority-Low, then port #1 will be turned on first, followed by port #2, etc. The highest PoE switch port number will be the first port to be turned off whenever the overall power consumption exceeds the maximum available power, again in accordance with PoE port number, while giving priority to Critical over High and High over Low.
- Critical: Highest level PoE port priority
- High: Mid-level PoE port priority
- Low: Lowest level PoE port priority
- LLDP: The LLDP configures the PoE port behavior with respect to LLDP packets from PD.
- Enable: PoE Parameters as PD power-request received through LLDP are processed
- Disable: PoE Parameters received through LLDP are ignored
- Cable Length: Cable length assist port power optimization allocation to remote PD advertising their power requirement over LLDP. Cable power loss for PD Type4 requesting 71.3W is assumed to be 18.7W for 100m cable length. So port max power will be set to 90W. However if PD is located only 30 meters away then port max power can be lowered to 76W freeing 14W for other PDs.
- max-10: Ethernet cable length is 10 meters or less
- max-30: Ethernet cable length is 30 meters or less
- max-60: Ethernet cable length is 60 meters or less
- max-100: Ethernet cable length is 100 meters or less
