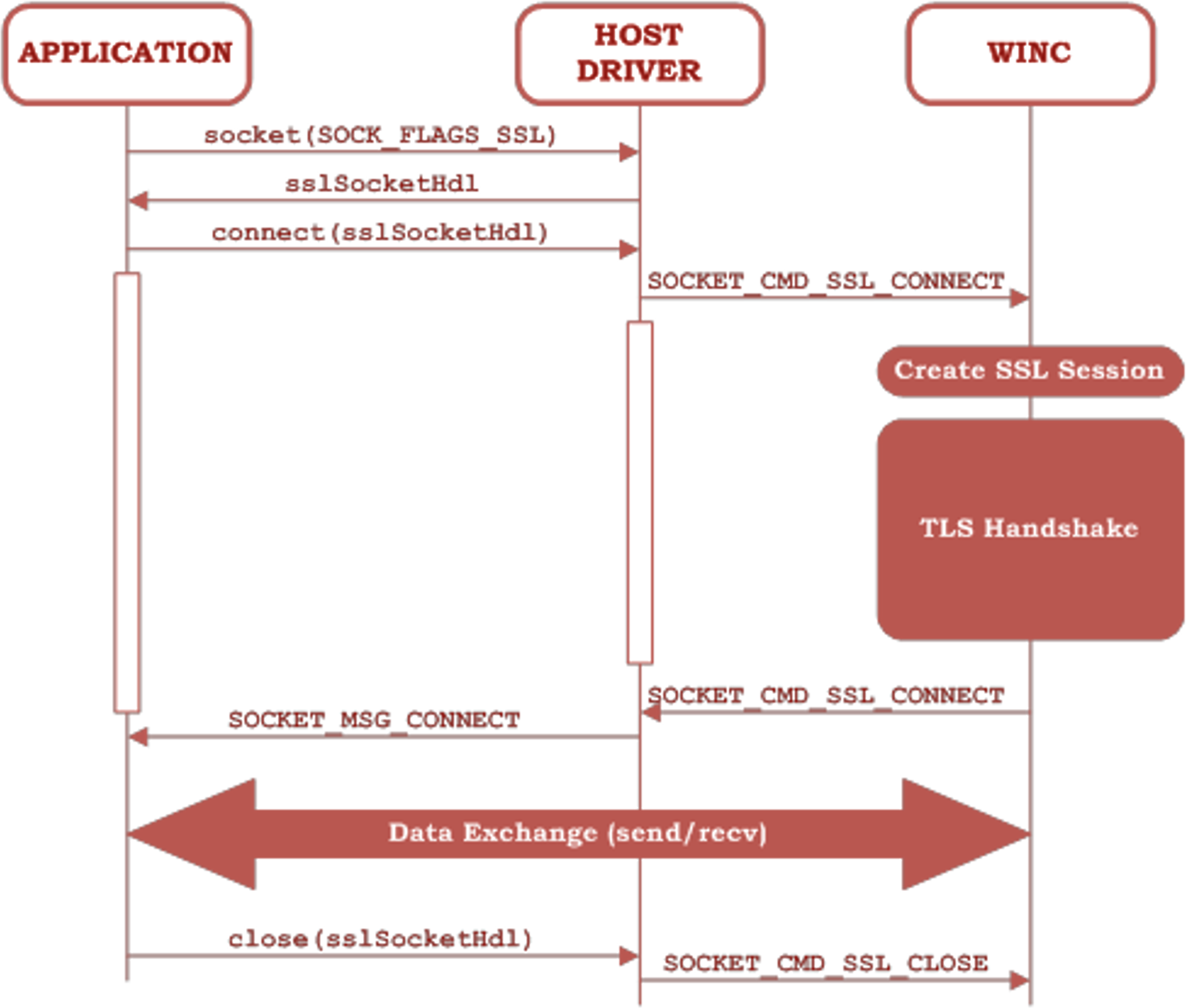
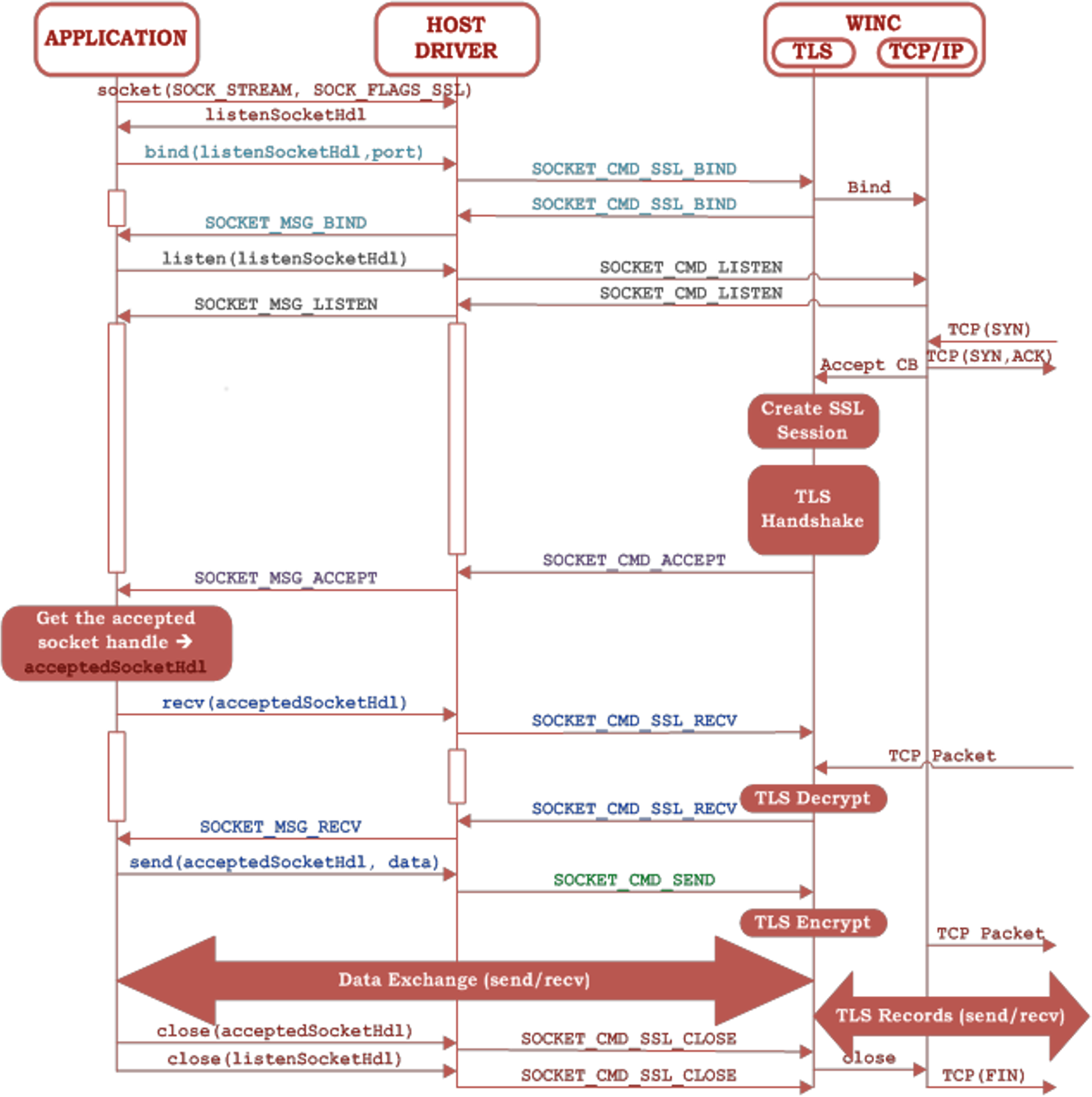
7.2 TLS Connection Establishment
From the application’s point of view, the TLS functionality is wrapped
behind the socket APIs. This hides the complexity of TLS from the application which can
use the TLS in the same way as the TCP (non-TLS) client and server. The main difference
between the TLS sockets and the regular TCP sockets is that the application sets the
SOCKET_FLAGS_SSL while creating the TLS client and server listening
sockets. The detailed sequence of TLS connection establishment is described in the
following figure.
Note:
- For proper TLS Client
operation, ensure that both
SOCKET_FLAGS_SSLflag and the correct port number is set in the TLS client application. For instance, an HTTP client application uses no flag when callingsocketAPI function andconnectto port 80. The same application source code becomes an HTTPS client application if you use the flagSOCKET_FLAGS_SSLand change the port number inconnectAPI to port 433. - For proper TLS server
operation, ensure that both
SOCKET_FLAGS_SSLflag and the correct port number is set in the TLS server application. For instance, an HTTP server application uses no flag when callingsocketAPI function andbindto port 80. The same application source code becomes an HTTPS server application, if you use the flagSOCKET_FLAGS_SSLand change the port number inbindAPI to port 443.