3.2.8.3 Net Socket Service
The Net Socket service provides network and socket services to the user
application. It includes DHCP server configuration for the Wi-Fi interface and API's for
socket operations such as open, read, write and close. It also provides 2 simultaneous
TLS configuration instances which can be used with a given socket communication tunnel.
The Net service API call syntax is provided
below:
SYS_RNWF_RESULT_t SYS_RNWF_NET_SockSrvCtrl( SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_SERVICE_t request, SYS_RNWF_NET_HANDLE_t);Net System Service Configuration in MCC
This section allows NET service basic configuration as mentioned below:
- Number of Sockets: Configure this field in the range of 1-2.
- Mode: Server/Client Mode Selection
- Ip Protocol: TCP/UDP protocol selection
- Ip Type: Select IP type : IPv4 / IPv6 Local / IPv6 Global.
- Server Address: Enter the respective server IP address.
- Socket Port: Socket port number.
- Enable TLS: Select to enable TLS Configuration option.
- Peer authentication
- Root CA / Server Certificate
- Device Certificate
- Device Key
- Device Key Password
- Server Name
- Domain Name Verify
- Domain Name
- Peer authentication
Note: Update the
SYS_RNWF_NET_NO_OF_CLIENT_SOCKETS
macro in sys_rnwf_net_service.h to reflect the number of client sockets
that the system can manage in the Server mode (supports a maximum of five clients). The Net service provides the following services for the user:
| Services/Options | Input Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
SYS_RNWF_NET_TLS_CONFIG_1 | TLS configuration list: CA name, Certificate name, Key name, Key password, server name | Use the TLS configuration 1 |
SYS_RNWF_NET_TLS_CONFIG_2 | TLS configuration list: CA name, Certificate name, Key name, Key password, server name | Use the TLS configuration 2 |
SYS_RNWF_NET_DHCP_SERVER_ENABLE | DHCP Configuration: Set IP, Pool start,
Parameter ID (Int) | Enable the DHCP server |
SYS_RNWF_NET_DHCP_SERVER_DISABLE | None | Disable the DHCP server |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_TCP_OPEN | None | Open TCP socket. Returns socket ID. |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_UDP_OPEN | None | Open UDP socket. Returns socket ID. |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_CLOSE | Socket ID (Int) | Close the socket |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_CONFIG | Socket ID | Configures the socket settings |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_SET_CALLBACK | Callback function handler | Register application callback for socket |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_SET_SRVC_CALLBACK | Callback function handler | Register application callback for sockets |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_GET_CALLBACK | Callback function handler | Get Function callback data |
The events that are returned in the Net socket service are provided below:
| Events | Response Components | Description |
|---|---|---|
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_CONNECTED |
Socket ID (Integer) | Reports the socket connected event |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_TLS_DONE | Socket ID (Integer) | TLS handshake done, on this event the TLS configuration instance can be re used for other TLS sessions |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_DISCONNECTED | Socket ID (Integer) | Socket disconnected |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_READ | Socket ID
(Integer) Length (Integer) | Reports the length of data available on the given socket ID |
SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_ERROR |
Socket ID (Integer) | Reports the socket error events |
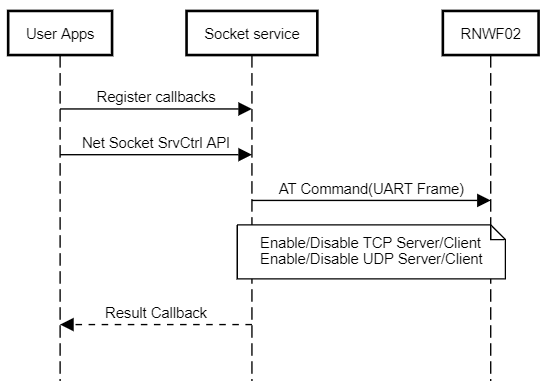
The basic net socket service sequence chart is provided below:
Socket Write
The socket service provides the write API for the TCP and UDP sockets. Following are the API
prototypes:
SYS_RNWF_RESULT_t SYS_RNWF_NET_TcpSockWrite( uint32_t socket, uint16_t length, uint8_t *input)SYS_RNWF_RESULT_t SYS_RNWF_NET_UdpSockWrite( uint32_t socket, uint8_t *addr, uint32_t port, uint16_t length, uint8_t *input)Socket
Read The socket service provides the read API for the TCP and UDP sockets. Following are the API prototypes:
int16_t SYS_RNWF_NET_TcpSockRead( uint32_t socket, uint16_t length, uint8_t *buffer)
int16_t SYS_RNWF_NET_UdpSockRead( uint32_t socket, uint16_t length, uint8_t *buffer)
The sample TCP socket example is provided below:
Some of the configurations can be configured by
MCC.
// ***************************************************************************** // ***************************************************************************** // Section: Included Files // ***************************************************************************** // ***************************************************************************** #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stddef.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* This section lists the other files that are included in this file.*/ #include "app_rnwf02.h" #include "user.h" #include "definitions.h" #include "configuration.h" #include "system/debug/sys_debug.h" #include "system/wifi/sys_rnwf_wifi_service.h" #include "system/inf/sys_rnwf_interface.h" #include "system/net/sys_rnwf_net_service.h" #include "system/sys_rnwf_system_service.h" /* Variable to check the UART transfer */ static volatile bool g_isUARTTxComplete = true; /*Shows the he application's current state*/ static APP_DATA g_appData; /*Application buffer to store data*/ static uint8_t g_appBuf[SYS_RNWF_IF_LEN_MAX]; /* TCP Socket Configurations*/ SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCKET_t g_tcpClientSocket = { .bind_type = SYS_RNWF_NET_BIND_TYPE0, .sock_port = SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_PORT0, .sock_type = SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_TYPE0, .sock_addr = SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_SERVER_ADDR0, .ip_type = SYS_RNWF_NET_IPV4, }; /* Application Wi-fi Callback Handler function */ void SYS_RNWF_WIFI_CallbackHandler(SYS_RNWF_WIFI_EVENT_t event,SYS_RNWF_WIFI_HANDLE_t wifiHandler) { uint8_t *p_str = (uint8_t *)wifiHandler; switch(event) { /* SNTP UP event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SNTP_UP: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("SNTP UP:%s\n", &p_str[2]); break; } /* Wi-Fi connected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_CONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Wi-Fi Connected \r\n"); break; } /* Wi-Fi disconnected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_DISCONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Wi-Fi Disconnected\nReconnecting... \r\n"); SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_WIFI_STA_CONNECT, NULL); break; } /* Wi-Fi DHCP complete event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_DHCP_IPV4_COMPLETE: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("DHCP Done...%s \r\n",&p_str[2]); if(SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_TYPE_IPv4_0 == SYS_RNWF_NET_IPV4) { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Connecting to server\r\n"); SYS_RNWF_NET_SockSrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_TCP_OPEN, &g_tcpClientSocket); } break; } /* Wi-Fi IPv6 DHCP complete event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_DHCP_IPV6_LOCAL_COMPLETE: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("IPv6 DHCP Local Done...%s \r\n",&p_str[2]); /*Local IPv6 address code*/ break; } case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_DHCP_IPV6_GLOBAL_COMPLETE : { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("IPv6 GLobal DHCP Done...%s \r\n",&p_str[2]); /*Global IPv6 address code*/ break; } /* Wi-Fi scan indication event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SCAN_INDICATION: { break; } /* Wi-Fi scan complete event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SCAN_DONE: { break; } default: break; } } /* Application NET socket Callback Handler function */ void SYS_RNWF_NET_SockCallbackHandler(uint32_t socket, SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_t event, SYS_RNWF_NET_HANDLE_t netHandler) { uint8_t *p_str = (uint8_t *)netHandler; if(g_tcpClientSocket.sock_master == socket) { switch(event) { /* Net socket connected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_CONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Connected to Server!\r\n" ); break; } /* Net socket disconnected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_DISCONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("DisConnected!\r\n"); SYS_RNWF_NET_SockSrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_CLOSE, &socket); break; } /* Net socket error event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_ERROR: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("ERROR : %s\r\n",p_str); break; } /* Net socket read event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_EVENT_READ: { uint8_t rx_data[1024]; int32_t rcvd_len; uint16_t rx_len = *(uint16_t *)p_str; memset(rx_data,0,1024); if((rx_len < 1024) && (rcvd_len = SYS_RNWF_NET_TcpSockRead(socket, rx_len, rx_data)) > 0) { rx_data[rx_len] = '\n'; SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Message from server : "); for(int i=0;rx_data[i];i++) SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("%c", rx_data[i]); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\n"); SYS_RNWF_NET_TcpSockWrite(socket, rx_len, rx_data); } break; } default: break; } } } /******************************************************************************* Function: void APP_Tasks ( void ) Remarks: See prototype in app.h. */ /* Maintain the application's state machine.*/ void APP_RNWF02_Tasks ( void ) { switch(g_appData.state) { /* Application's state machine's initial state. */ case APP_STATE_INITIALIZE: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Start Of Application\r\n"); DMAC_ChannelCallbackRegister(DMAC_CHANNEL_0, APP_RNWF_usartDmaChannelHandler, 0); SYS_RNWF_IF_Init(); g_appData.state = APP_STATE_REGISTER_CALLBACK; break; } /* Register the necessary callbacks */ case APP_STATE_REGISTER_CALLBACK: { SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_GET_MAN_ID, g_appBuf); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nManufacturer = %s\r\n", g_appBuf); SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SW_REV, g_appBuf); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nSoftware Revision:- %s\r\n", g_appBuf); SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SrvCtrl(SYS_RWWF_SYSTEM_GET_WIFI_INFO, g_appBuf); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nWi-Fi Info:- \r\n%s\r\n", g_appBuf); SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_GET_CERT_LIST, g_appBuf); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nCerts on RNWF:- \r\n%s\r\n", g_appBuf); SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SYSTEM_GET_KEY_LIST, g_appBuf); SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nKeys on RNWF:- \r\n%s\r\n", g_appBuf); /* RNWF Application Callback register */ SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SET_CALLBACK, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_CallbackHandler); SYS_RNWF_NET_SockSrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_NET_SOCK_SET_CALLBACK, SYS_RNWF_NET_SockCallbackHandler); /* Set Regulatory domain/Country Code */ const char *regDomain = SYS_RNWF_COUNTRYCODE; SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nSetting regulatory domain : %s\r\n",regDomain); SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SET_REGULATORY_DOMAIN, (void *)regDomain); /* Wi-Fi Connectivity */ SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PARAM_t wifi_sta_cfg = {SYS_RNWF_WIFI_MODE_STA, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_STA_SSID, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_STA_PWD, SYS_RNWF_STA_SECURITY, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_STA_AUTOCONNECT}; SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("\r\nConnecting to : %s\r\n",SYS_RNWF_WIFI_STA_SSID); SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_PARAMS, &wifi_sta_cfg); g_appData.state = APP_STATE_TASK; break; } /* Run Event handler */ case APP_STATE_TASK: { SYS_RNWF_IF_EventHandler(); break; } default: { break; } } }
