3.4 PUF States
The PUF module provides several operations which are triggered by software commands or hardware events. For several reasons (e.g., security, etc.), not all operations are available at all times. The following figure illustrates the operation capabilities.
For brevity, the operations related to keys, such as Get Key, Wrap, Wrap Generated Random, and Unwrap, are grouped as Key operations.
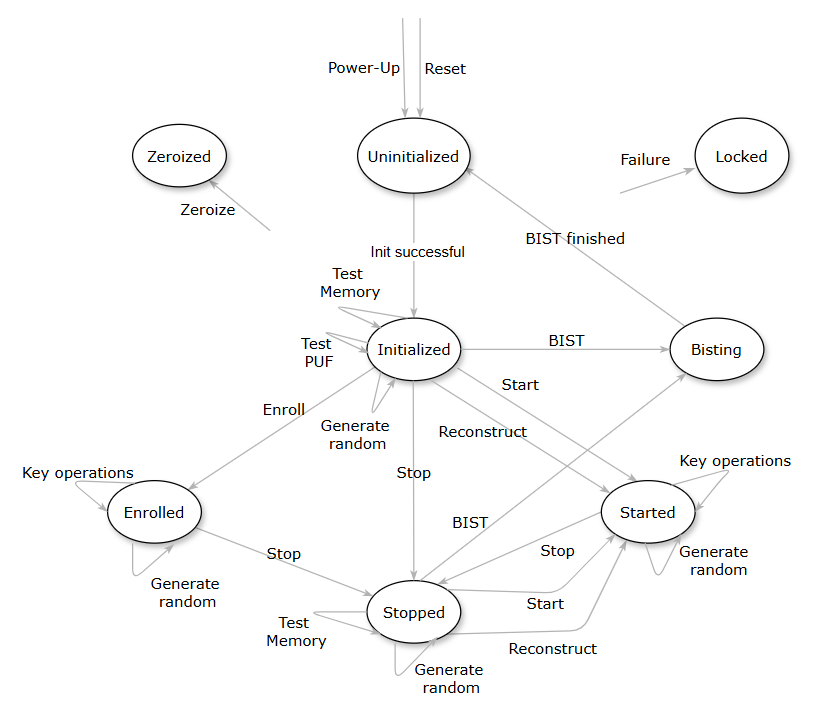
After power-up, the PUF module begins in the Uninitialized state until the PUF driver runs the initialization sequence (see Initialization Operation).
When initialization finishes successfully, the PUF module moves to the Initialized state. It moves to the Locked state on failure.
In the Initialized state, several operations can be performed: BIST, Test PUF, Test SRAM, Generate Random, Enroll, Start, Reconstruct, and Stop.
DRV_PUF_Disable function in the PUF driver). This is
valid in all states.After a successful Enroll operation (see Enroll Operation), the PUF module is in the Enrolled state and can perform a Generate Random operation, key operations or a Stop operation (when no further actions are required at that moment).
After a successful Start (see Start Operation) or Reconstruct (see Reconstruct Operation) operation, the PUF module is in the Started state. In this state, a Generate Random operation, key operations or a Stop operation can be done.
A Stop operation (see Stop Operation) brings the PUF module to the Stopped state. In this state, no sensitive data is present in the module and the following operations can be performed: BIST, Test Memory, Generate Random, Start, and Reconstruct.
When in Started or Enrolled state, key operations can be performed (see corresponding chapters). After such an operation is complete, the PUF module returns to the state it was in before the operation.
In an Initialized, Enrolled, Started or Stopped state, random data can be generated with the Generate Random command (see Generate Random Operation).
In Initialized or Stopped state, the PUF SRAM can be tested with the Test Memory operation (see Test Memory Operation). Details on the memory test are provided in PUF SRAM Test.
With the Test PUF operation (see Test PUF Operation), diagnostic information about the PUF quality is collected and the score is returned. This operation is intended for production test purposes. It can only be executed once per reset or power cycle. Details on the diagnostics are provided in PUF Diagnostics.
The Zeroize command (see Zeroize Operation) erases all critical security parameters and prevents the PUF module from executing any more commands by entering the Zeroized state. The only way to leave this state consists in power-cycling the device, which puts the PUF module in Uninitialized state.
If an operation is unsuccessful, the PUF module returns to the state it was in when the command was issued.
If a failure (i.e., unrecoverable error) occurs during any of the above-mentioned operations (including Initialization and Zeroize), the PUF module goes to the Locked state. In this state, no commands can be executed except Zeroize.
Errors and failures are detailed in PUF Error Handling.
A BIST operation (see PUF Built-In Self-Test (BIST)) can be performed when the PUF module is in Initialized or Stopped state.
During BIST, no other operations can be performed. After BIST has finished, the PUF module enters the Uninitialized state. It behaves the same way as for a reset.
- Input: data or settings
- Output: data (secure output – HSM Lite – or output parameter) or information (output parameter)
| Operation | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | Addresses to PUF module and initial register configuration | None |
| Enroll | None | Activation code and PUF score |
| Start | Activation code | PUF score |
| Reconstruct | Activation code | PUF score |
| Stop | None | None |
| Get Key | Scope, context, destination, and key size | Key in selected destination |
| Wrap Generated Random | Scope, context, and key size | Key code |
| Wrap | Scope, context, key size, and key | Key code |
| Unwrap | Key code and destination | Key in selected destination |
| Generate Random | Destination and size | Random data in selected destination |
| Test Memory | None | None |
| Test PUF | None | PUF score |
| Zeroize | None | None |
| BIST | None | None |
