18 Introduction
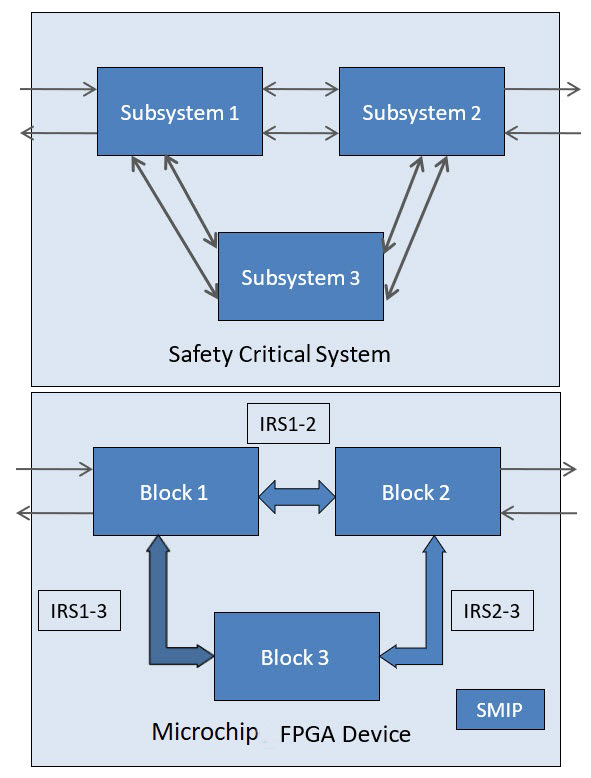
(Ask a Question)This guide describes the design separation methodology required to implement security and safety-critical applications. For a system to be secure and reliable, all critical subsystems in the design should be independent of each other.
Traditionally, a system with security and safety-critical requirements is built with each critical subsystem implemented using multiple integrated circuits (ICs). With each critical subsystem as an independent IC, fault and reliability analysis is simplified. In a traditional Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) design, netlists generated for place-and-route often are flattened for efficient placement. Design functions from various parts of the design hierarchy may share physical resources. To meet critical security and safety application requirements, critical subsystems within an FPGA design might need to be isolated to simplify failure analysis and prevent propagation of faults from one subsystem adversely affecting another.