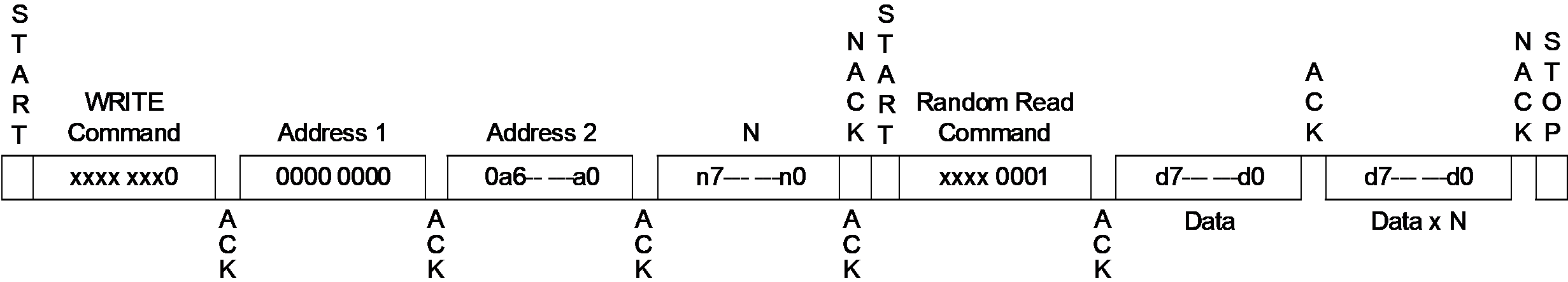8.8.1 Functional
The Random Read command ($B1) allows reading of data from the device’s configuration memory or the currently selected user zone (see section 8.10 System Write: $B4 for information on how to select a user zone).
The Random Read command provides the host with the ability to sequentially clock data from the device, starting from a specified address. The host must first specify the start address to read from in the memory by executing a “dummy” operation. The host does this by clocking in the four bytes of the write command and then following them with a Start condition instead of a data byte. At this point, the device’s internal logic is pointing to the address from the aborted write operation. The host may then issue the Random Read command byte ($B1), to which the device will respond with the EEPROM byte at the current address location and then increment the internal address by one. The device will continue to sequentially send out bytes as long as the host acknowledges each byte with an ACK. During this operation, the address will roll over from the last byte of the current zone to the first byte of the same zone. The host terminates the Random Read by issuing a NACK signal instead of an ACK.