43.3.6.6 Quick Dual Multiplying by Two Scalar Numbers and Two Points
Purpose
This service is used to multiply two points by two integral constants K1 and K2, and then provide the addition of these multiplications results.
How to Use the Service
Description
This service processes the dual Multiplying by two scalar numbers:
PtC = K1 × PtA + K2 × PtB
In this computation, the following parameters need to be provided:
- A the first input point is filled in projective coordinates (X,Y,Z) (pointed by {pu1PointABase,(3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WA-2))}). This point can be the Infinite Point.
- B the 2nd input point is filled in projective coordinates (X,Y,Z) (pointed by {pu1PointBBase,(3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WB-2))}). This point can be the Infinite Point.
- P the modulus filled and Cns the Fast Modular Constant filled (pointed by {pu1ModCnsBase,2*u2ModLength + 16})
- The a parameter filled and the workspace not initialized (pointed by {pu1AWorkBase, 9*u2ModLength +48}
- KAB the scalar numbers (pointed by {pu1KABBase, 2*u2KLength +8})
- The options
are set by the u2Options input parameter, which is composed
of:
- wA: Size of window for Point A between 2 and15
- wB: Size of window for Point B between 2 and15
- PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_SCAL_IN_CLASSIC_RAM flag: to set only if the scalars are entirely in Classic RAM with no part in PUKCC RAM
The resulting C point is represented in projective coordinates (X,Y,Z) and is stored at (pu1AWorkBase + u2ModLength + 4). This point can be the Infinite Point.
Parameters Definition
WA is the Point A window size and WB is the Point B window size (see Options below for details).
| Parameter | Type | Direction | Location | Data Length | Before Executing the Service | After Executing the Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pu1ModCnsBase | pu1 | I | Crypto RAM | 2 * u2ModLength + 16 | Base of modulus P, Base of Cns | Base of modulus P, Base of Cns |
| u2Option | u2 | I | – | – | Option related to the called service (see below) | – |
| u2ModLength | u2 | I | – | – | Length of modulus P | Length of modulus P |
| pu1KABBase | pu1 | I | Any RAM | 2 * u2KLength + 8 | Scalar numbers used to multiply the points A and B | Unchanged |
| u2KLength | u2 | I | – | – | Length of scalars KA and KB | Length of scalars KA and KB |
| pu1PointABase | pu1 | I/O | Crypto RAM |
(3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WA-2)) (1) | Input point A (projective coordinates) | Unchanged |
| pu1PointBBase | pu1 | I | Crypto RAM |
(3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WB-2)) (2) | Input point B (projective coordinates) | Unchanged |
| pu1AWorkBase | pu1 | I | Crypto RAM | 9*u2ModLength + 48 | Parameter a of the elliptic curve | Resulting point C (projective coordinates) in pu1AWorkBase Base + u2ModLength + 4 |
- The precalculus table size for the point A is calculated from chosen window size “WA”.
- The precalculus table size for the point B is calculated from chosen window size “WB”.
Options
The options are set by the u2Options input parameter, which is composed of:
- the mandatory windows sizes WA and WB
- the indication of the presence of the scalars in system RAM
The u2Options number is calculated by an “Inclusive OR” of the options. Some Examples in C language are:
// Scalars are in system RAM// The Point A window size is 3// The Point B window size is 4PUKCL(u2Options) = PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_SCAL_IN_CLASSIC_RAM |PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_A_VAL_TO_OPT(3) |PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_B_VAL_TO_OPT(4);// Scalars are in the PUKCC Cryptographic RAM// The Point A window size is 2// The Point B window size is 5PUKCL(u2Options) = PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_A_VAL_TO_OPT(2) |PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_B_VAL_TO_OPT(5);
For this service, many window sizes are possible. The window sizes in bits are those of the windowing method used for the scalar multiplying.
The choice of the window sizes is a balance between the size of the parameters and the computation time:
- Increasing the window size increases the precomputation table size.
- Increasing the window size to the optimum reduces the computation time.
The following table details the size of the point and the precomputation table, depending on the chosen window size option.
| Option Specified | Size of the Point and the Precomputation Table |
|---|---|
| PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_A_VAL_TO_OPT(WA) WA in [2, 15] | (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WA-2)) |
| PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_WINSIZE_B_VAL_TO_OPT(WB) WB in [2, 15] | (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WB-2)) |
The scalars can be located in PUKCC RAM or in system RAM. If both scalars are entirely in system RAM with no part in PUKCC RAM this can be signaled by using the option PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_SCAL_IN_CLASSIC_RAM. In all other cases this option must not be used.
The following table describes this option.
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
PUKCL_ZPECCMUL_SCAL_IN_CLASSIC_RAM |
The scalars can be located in Crypto RAM or in system RAM. If both scalars are entirely in system RAM with no part in Crypto RAM this can be signaled by using this option . In all other cases this option must not be used. |
Code Example
PUKCL_PARAM PUKCLParam;
PPUKCL_PARAM pvPUKCLParam = &PUKCLParam;
PUKCL(u2Option) = <Configure scalar numbers location and windows sizes>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(pu1ModCnsBase) = <Base of the ram location of P and Cns>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(u2ModLength) = <Byte length of P>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(u2KLength) = <Byte length of scalars>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(pu1PointABase) = <Base of the ram location of the A point>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(pu1PointBBase) = <Base of the ram location of the B point>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(pu1AWorkBase) = <Base of the ram location of the parameter A of the elliptic curve and workspace>;
PUKCL_ZpEccQuickDualMulFast(pu1KABBase) = <Base of the ram location of the scalar numbers KA and KB>;
...
// vPUKCL_Process() is a macro command, which populates the service name
// and then calls the library...
vPUKCL_Process(ZpEccQuickDualMulFast, pvPUKCLParam);
if (PUKCL(u2Status) == PUKCL_OK)
{
...
}
else // Manage the error
Constraints
No overlapping between either input and output are allowed. The following conditions must be avoided to ensure that the service works correctly:
- pu1ModCnsBase,pu1PointABase, pu1PointBBase, pu1AWorkBase, pu1KABBase are not aligned on 32-bit boundaries
- {pu1ModCnsBase, 2*u2ModLength + 16}, {pu1PointABase, (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) *(2(WA-2))}, {pu1PointBBase, (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WB-2))} or { pu1AWorkBase, 9*u2ModLength + 48} are not in PUKCC RAM
- u2ModLength is either: < 12, > 0xffc or not a 32-bit length
- Alloverlapping between {pu1ModCnsBase, 2*u2ModLength + 16}, {pu1PointABase, (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WA-2))}, {pu1PointBBase, (3*(u2ModLength + 4)) * (2(WB-2))} or {pu1AWorkBase, 9*u2ModLength + 48}.
Parameters Placement
The parameters’ placement is described in the following figures.
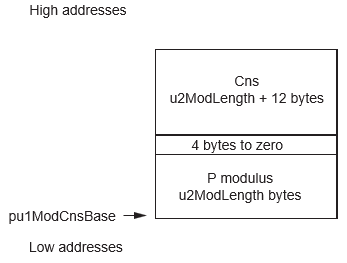
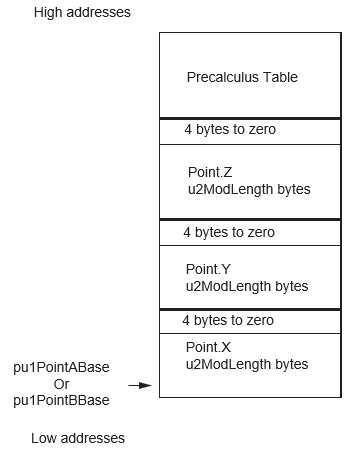
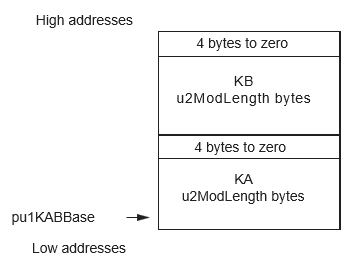
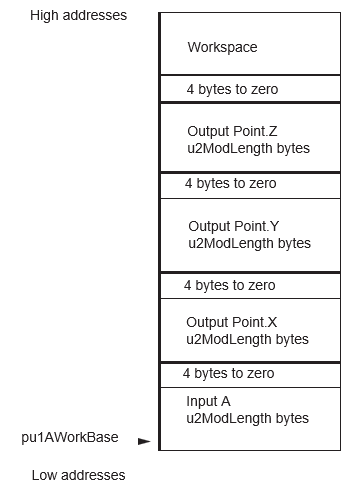
Status Returned Values
| Returned Status | Importance | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| PUKCL_OK | – | The computation passed without problem. |
