6.6 Transceiver Selection and Configuration Page
-
Region - the frequency of transmission depends on the region in which the system operates
-
Frequency - The frequency (or Channel) at which the transmission or reception are done
-
Data Rate - the rate at which the packet frames are transferred
-
Antenna Diversity - In a multi-path environment, several versions of the same signal with different phases, delays, and attenuations will be added together at the receiver location, so there is always the possibility that at some locations, the signals could cancel each other out almost entirely. One way to overcome the multi-path issue is to use the receiver antenna diversity technique. In this method, two antennas are used instead of one in the receiver. This way, if one antenna is in a multi-path null (also known as deep-fading region), the other antenna has a good chance of being outside the deep-fading region. The receiver can switch between these two antennas to escape from a multi-path null. Few transceivers (AT86RF231, AT86RF232, AT86RF233, and AT86RF212B) support antenna diversity.
-
Device Address (Short Address) - Address of the device on the network that the current device (node) will be part of
-
PAN ID of the device - PAN ID of the network in which the current device (node) will be part of
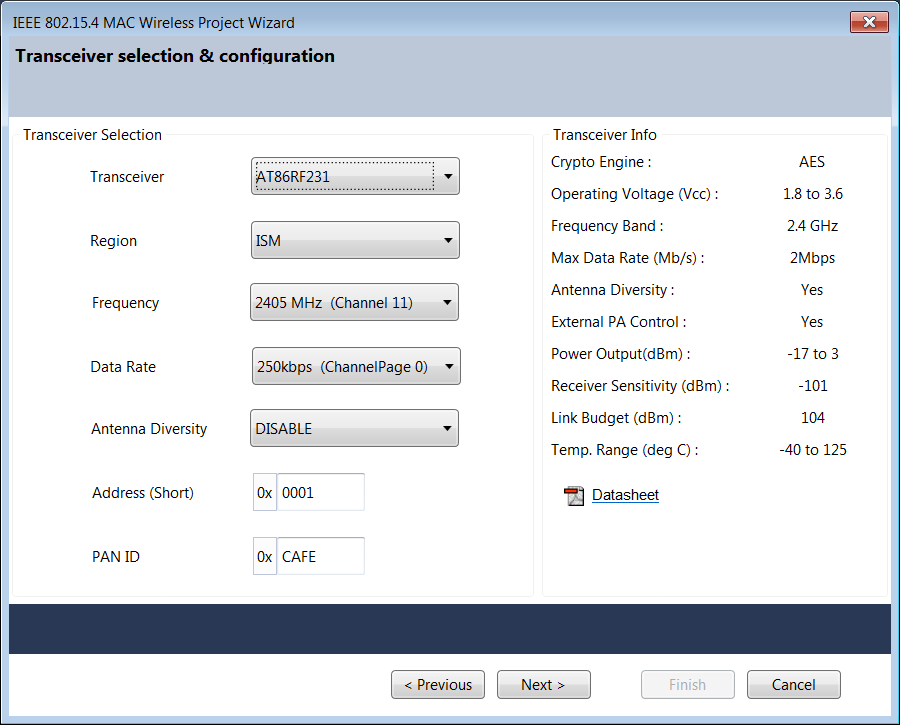
Once the desired parameters are set, click on the button Next to view Transmit/Receive Page.
