1.1 Power Supplies
(Ask a Question)The following illustration shows the typical power supply requirements for PolarFire SoC devices, and the recommended connections of power rails when every part of the device is used in a system. For more information on decoupling capacitors associated with individual power supplies, see PolarFire SoC Decoupling Capacitors.
To calculate the number of decoupling capacitors, it is important to know the target impedance of the power plane. Target impedance is calculated as follows:
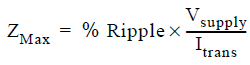
Where,
Vsupply: Supply voltage of the power plane.
% Ripple: Percentage of ripples that is allowed on the power plane. See PolarFire SoC Datasheet for more information about ripple in Recommended Operating Conditions table.
Itrans: Transient current drawn on the power plane. The transient current is half of the maximum current. Maximum current is taken from the power calculator sheet.
Zmax: Target impedance of the plane.
For the PolarFire SoC device to operate successfully, power supplies must be free from unregulated spikes and the associated grounds must be free from noise. All overshoots and undershoots must be within the absolute maximum ratings provided in the PolarFire SoC Datasheet.
The following table lists the various power supplies required for PolarFire SoC FPGAs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| XCVR_VREF | Voltage reference for transceivers |
| VDD_XCVR_CLK | Power to input buffers for the transceiver reference clock |
| VDDA25 | Power to the transceiver PLL |
| VDDA1 | Power to the transceiver TX and RX lanes |
| VSS | Core digital ground |
| VDD2 | Device core digital supply |
| VDDI3 (JTAG Bank) | Power to JTAG bank pins |
| VDDI53 | VDDI5 power to MSS SGMII banks and MSS dedicated clocks. |
| VDDI2 | VDDI2 power to MSS peripheral banks |
| VDDI4 | Power to MSS peripheral banks |
| VDDI6 | Power to MSS DDR banks |
| VDDIx (GPIO Banks) | Power to GPIO bank pins |
| VDDIx (HSIO Banks) | Power to HSIO bank pins |
| VDD25 | Power to corner PLLs and PNVM |
| VDD18 | Power to programming and HSIO auxiliary supply |
| VDDAUXx | Power to GPIO auxiliary supply |
- VDDA—This supply can be powered to 1.0V or 1.05V. For more information, see the Recommended Operating Conditions section in PolarFire SoC Datasheet. This is a quiet supply for the device. One method is to use a Linear regulator to ensure the supply is quiet.
- VDD—This supply can be powered to 1.0V or 1.05V. For more information, see the Recommended Operating Conditions section in PolarFire SoC Datasheet.
- VDDI5 must be powered-up before or along with VDD. VDDI5 must reach its datasheet minimum value before VDD reaches a functional level and also before the time when MSS is ready to execute its first instruction (referred to as TCPU in the datasheet). VDDI5 calibration is done by the Firmware. Hence, there is no support for setting the calibration time of VDDI5 in Libero SoC.
- Internal VREF—is not subjected to PCB, package inductance, and capacitance loss. These changes provide the highest performance and can be programmed as required by DDR controller.
- External VREF—is fixed and cannot be programed as required. The
PCB, package inductance, and capacitance impact the VREF performance.
If VDDI and VDDAUX must be configured to the same voltage of 2.5V or 3.3V, ensure both VDDI and VDDAUX are supplied from the same regulator. Do not use different regulators to source these rails. This prevents any voltage variations between VDDI and VDDAUX. In this case, the board must not supply the VDDI and VDDAUX from individual voltage supplies.
When a GPIO bank requires the VDDI to be less than 2.5V (1.2V, 1.5V, or 1.8V), the VDDAUX for that bank must be tied to 2.5V supply irrespective of the VDDI supply. VDDI requires a separate supply for the specific I/O type such as 1.5V or 1.8V.
Note:- The on-chip Power-on-Reset (POR) circuitry requires the VDD, VDD18, and VDD25 supplies to ramp monotonically from 0V to the minimum recommended operating voltage.
- You must initiate the I/O calibration only when both the VDDA and XCVR_VREF supplies are up.
For a detailed pin description, see PolarFire SoC FPGA Packaging and Pin Descriptions User Guide.
