4.2 Green Ethernet—Port Power Saving Configuration
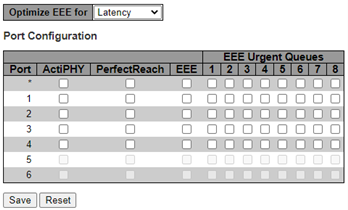
The Port Power Saving Configuration page allows you to configure the port power savings features. The following figure shows the Port Power Saving configuration.
EEE is a power saving option that reduces power usage when there is low or no traffic utilization. EEE works by powering down circuits when there is no traffic. When a port gets the data transmitted, then all circuits are powered-up. EEE works for ports in the Auto-Negotiation mode, where the port is negotiated to either 1G or 100 Mbit full Duplex mode.
The Port Power Saving Configuration page has the following parameters:
- Optimize EEE Mode: The switch can be set to optimize EEE for either best power saving or least traffic latency
- Port: The switch port number of the logical port
- ActiPHY: Link down power savings enabled. ActiPHY works by lowering the power for a port when there is no link. The port is powered up for a short moment to determine if the cable is inserted.
- PerfectReach: Cable length power savings enabled. PerfectReach works by determining the cable length and lowering the power for ports with short cables.
- EEE: Controls if EEE is enabled for this switch port. For maximizing power savings, the circuit is not started when transmit data is ready for a port but is queued until a burst of data is ready to be transmitted. This gives some traffic latency. If desired, it is possible to minimize the latency for specific frames by mapping the frames to a specific queue (mapping done with QOS), and then mark the queue as an urgent queue. When an urgent queue gets data to be transmitted, the circuits are powered-up at once and the latency is reduced to the wakeup time.
- EEE Urgent Queues: Queues that are set activate transmission of frames as soon as data is available. Otherwise, the queue postpones transmission until a burst of frames can be transmitted.
