4.19 Mirroring Configuration
Mirroring is a feature for switched port analyzer. The administrator can use Mirroring to debug network problems. The selected traffic can be mirrored or copied on a destination port where a network analyzer can be attached to analyze the network traffic. Remote Mirroring is an extended function of Mirroring. It can extend the destination port in another switch so that the administrator can analyze the network traffic on the other switches. If you want to get the tagged mirrored traffic, you must set VLAN egress tagging as Tag All on the reflector port. On the other hand, if you want to get untagged mirrored traffic, you must set VLAN egress tagging as Untag ALL on the reflector port.
In the following figure, port #5 Tx and Rx are configured to be mirrored over port #1.
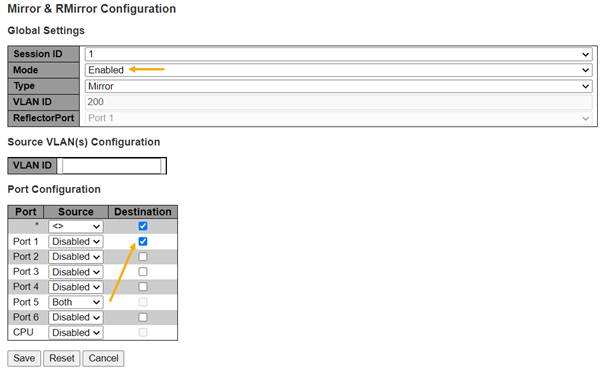
The Mirror and RMirror Configuration page has the following parameters:
- Global Settings
- Session ID: Select session ID (not to be confused with port number) to configure
- Mode: Enable/Disable session mirroring or Remote Mirroring session function
- Type: Select switch mirror
type
- Mirror: The switch is running in Mirror mode. The source port(s) and destination port are located on this switch.
- Source: The switch is a source node for monitor flow. The source port(s), reflector port are located on this switch.
- Rmirror Destination: The switch is an end node for monitor flow. The destination port(s) is located on this switch.
- VLAN ID: The VLAN ID points out the destination, where the monitor packet copies to. The default VLAN ID is 200.
- ReflectorPort: The reflector port is a
method to redirect the traffic to Remote Mirroring VLAN. Any device connected to a
port set as a reflector port loses connectivity until the Remote Mirroring is
disabled. In the Stacking mode, you must select switch ID to select the correct
device. If you shut down a port, it cannot be a candidate for Reflector port. If you
shut down the port which is a Reflector port, then the remote mirror function cannot
work.Note:
- The reflector port must select only on Source switch type
- The reflector port must disable MAC Table learning and STP
- The reflector port only supports pure copper ports
- Source VLAN (s) Configuration: The switch
can support VLAN-based Mirroring. To monitor some VLANs on the switch, set the
selected VLANs on this field.Note: The Mirroring session has either ports or VLANs as sources, but not both.
- Remote Mirroring Port Configuration: The
following table is used for port role selecting:
- Port: The logical port for the settings contained in the same row
- Source: Select mirror mode:
- Disabled: Neither frames transmitted, nor frames received are mirrored
- Both: Frames received and frames transmitted are mirrored on the Destination port
- Rx only: Frames received on this port are mirrored on the Destination port. Frames transmitted are not mirrored.
- Tx Only: Frames transmitted on this port are mirrored on the Destination port. Frames received are not mirrored.
- Destination: Select destination port. This
checkbox is designed for mirror or Remote Mirroring. The destination port is a
switched port where you receive a copy of traffic from the source port.Note:
- On the Mirror mode, the device only supports one destination port.
- The destination port must disable MAC table learning
Configuration Guideline for All Features
When the switch is running on Remote Mirroring mode, the administrator must also check if other features are enabled or disabled. For example, the administrator is not disabled the MSTP on reflector port. All monitor traffic is blocked on reflector port. The following table lists all recommended settings.
| Network Feature | Impact3 | Reflector Port | Intermediate Port | Destination Port | Remote Mirroring VLAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arp_inspection | High | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| acl | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — |
| dhcp_relay | High | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| dhcp_snooping | High | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| ip_source_guard | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — |
| ipmc/igmpsnp | Critical | — | — | — | un-conflict |
| ipmc/mldsnp | Critical | — | — | — | un-conflict |
| lacp | Low | — | — | Disabled2 | — |
| lldp | Low | — | — | Disabled2 | — |
| mac learning | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — |
| mstp | Critical | Disabled | — | Disabled2 | — |
| mvr | Critical | — | — | — | un-conflict |
| nas | Critical | Authorized1 | Authorized1 | Authorized1 | — |
| psec | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — |
| qos | Critical | Unlimited1 | Unlimited1 | Unlimited1 | — |
| upnp | Low | — | — | Disabled2 | — |
| mac-based vlan | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| protocol-based vlan | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| vlan_translation | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — |
| voice_vlan | Critical | Disabled1 | Disabled1 | — | — |
| mrp | Low | — | — | Disabled2 | — |
| mvrp | Low | — | — | Disabled2 | — |
- Must
- Optional
- Impact—Critical/High/Low
- Critical 5 packets > 0 packet
- High 5 packets > 4 packets
- Low 5 packets > 6 packets
