5.1 Bootstrap Resistor Selection
Considering Figure 5-1, when the low side MOSFET (Q2, Q4, or Q6) turns on, VS pulls to GND and the bootstrap capacitor (CB1, CB2, and CB3) is charged. When the high side MOSFET (Q1, Q3, and Q5) is turned on, VS swings above VCC and the charge on the bootstrap capacitor (CBx) provides current to drive the IC high side gate driver. The first charge of CBx from VCC through the bootstrap resistor (RB1, RB2, and RB3) and bootstrap diode (DB1, DB2, and DB3) occurs when power is first applied and low side turns on the first time. At this time the charge current is the largest as, typically, CBx is not discharged fully at each cycle during normal operation.
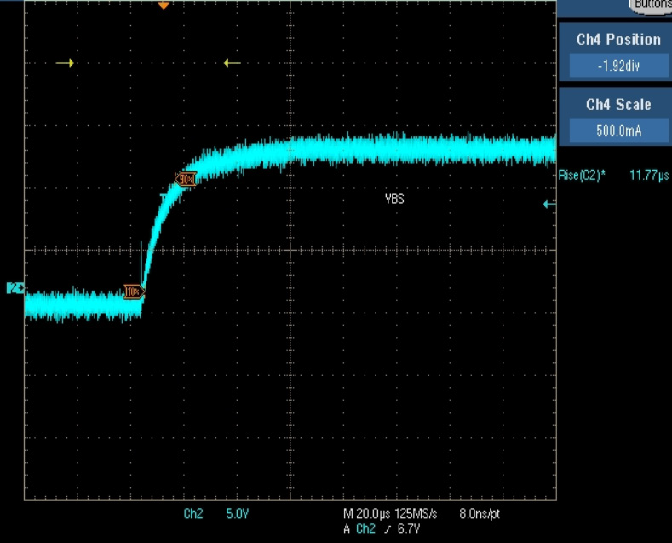
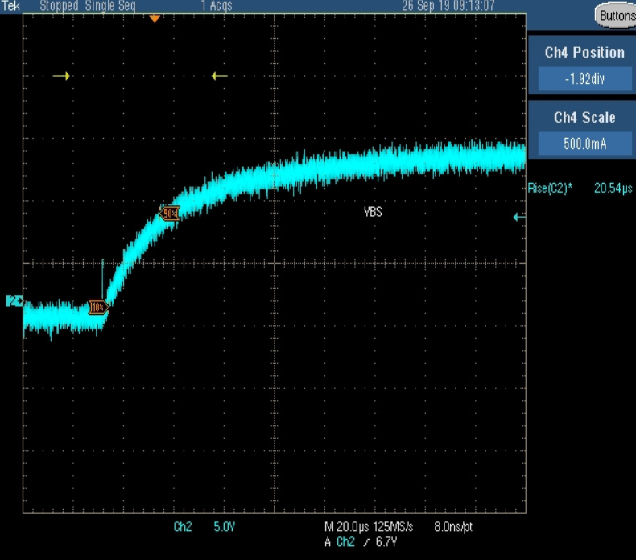
A bootstrap resistor (RBx) is included in the bootstrap circuit to limit the inrush current that charges CBx when VS pulls below VCC. This inrush current is largest with the first charge. Limiting inrush current is desirable to limit noise spike on VS and COM, potentially causing shoot-through. The amplitude and length of time of the inrush current is determined mostly by the component value of RBx and CBx, as well as the VCC level. The aim in resistor selection for the application is to slow down the inrush current but have limited effect on the RC time constant of charging CBx.
Typically, values for RBx are 3Ω to 10Ω, enough to dampen the inrush current but have little effect on the VBS turn ON. Below are some scopeshots illustrating the effect of different RBx values.
 |
 |
 |
 |
