5.1.2.4 BLE Deep Sleep Advertising
This section explains how to enable “Deep Sleep” mode with BLE Advertisements on the WBZ351 Curiosity board using the MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC). In this application example, the Deep Sleep advertisement interval will be set to 1 second. This interval dictates the application Deep Sleep time.
Users can choose to either run the precompiled Application Example hex file provided on the WBZ351 Curiosity Board or follow the steps to develop the application from scratch.
These examples build upon one another. It is recommended to follow the examples in sequence to understand the basic concepts before progressing to the advanced topics.
Recommended Readings
-
Getting Started with Application Building Blocks – See Building Block Examples from Related Links.
-
Getting Started with Peripheral Building Blocks – See Peripheral Devices from Related Links.
-
FreeRTOS and BLE Stack Setup – See Peripheral - FreeRTOS BLE Stack and App Initialize from Related Links.
-
BLE Software Specification – See MPLAB® Harmony Wireless BLE in Reference Documentation from Related Links.
- See Low Power Design on PIC32CX-BZ3 Devices from Related Links.
Hardware Requirement
| S. No. | Tool | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | WBZ351 Curiosity Board | 1 |
| 2 | Micro USB cable | 1 |
| 3 | Android/iOS Smartphone | 1 |
| 4 | (Optional) Power
Debugger(1)/Multimeter/Oscilloscope to measure power
Note:
| 1 |
SDK Setup
Refer to Getting Started with Software Development from Related Links.
Software
To install Tera Term tool, refer to the Tera Term web page in the Reference Documentation from Related Links.
Smartphone App
Microchip Bluetooth® Data (MBD) iOS/Android app available in stores.
Programming the Precompiled Hex File or Application Example
Using MPLAB® X IPE:
- Import and program the
precompiled hex file:
<Discover Path>\wireless_apps_pic32cxbz3_wbz35\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\deep_sleep_adv\hex\deep_sleep_adv.X.production.signed.hex - For detailed steps, refer to
Programming a Device in MPLAB® IPE in
Reference Documentation from Related Links.Note: Ensure to choose the correct Device and Tool information.
Using MPLAB® X IDE:
- Perform the following the steps mentioned in Running a Precompiled Example. For more information, refer to Running a Precompiled Application Example from Related Links.
- Open and program the application:
<Discover Path>\wireless_apps_pic32cxbz3_wbz35\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\ deep_sleep_adv\firmware\deep_sleep_adv.X - For more details on how to find the Discover path, refer to Download Application Example from Discover in Running a Precompiled Application Example from Related Links.
Demo Description
This application example enables users to enter Deep Sleep mode while transmitting Connectable, Undirected BLE Advertisements. On power-on reset, the application will enter Deep Sleep mode. When USR-BTN1 (SW2) is pressed, the device on-board GREEN LED starts blinking to denote the start of advertisements. The device will then enter Deep Sleep mode periodically based on the advertisement interval of 1 second. When the device connects with the mobile app, the onboard LED starts to glow solid, which indicates that the connection is established and the device will enter Standby Sleep mode during Idle state.
Testing
- Using a micro USB cable, connect the Debug USB on the Curiosity board to a PC
- Program the precompiled hex file or application example as mentioned. Upon flashing, there will be no indication on the board since the device entered Deep Sleep mode.
- Press USR-BTN1 (SW2) on the board to start Deep Sleep Advertising
- Launch the MBD mobile app and select the BLE Smart sub app to see the scan results. Device name “BLE_DSADV” will appear.
Current Consumption Measurement
Hardware modification
Connect a Multimeter/Power Debugger/Oscilloscope to Power Measurement Header J5. If using a Power Debugger, users can use Data Visualizer to measure the current consumption.
Current measured in Deep sleep mode is around 1.9 uA.
Current measured in Deep sleep + Advertising mode is around 130 uA average.
Users of this early adopter package should go through the known issues document and understand the limitations, if any, with the current low power mode implementation.
Developing the application from scratch
There are two possible ways to develop this application. In the following section, users can make use of the import method available in the MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC). This is the easiest and quickest way to recreate the application with the help of an import component configuration. In the second section, users can experience the complete application development from scratch using the MCC.
Developing this Application using MPLAB Code Configurator Import method
-
Create a new harmony project. For more details, see Creating a New MCC Harmony Project from Related Links.
Setup the basic components and configuration required to develop this application, import component configuration:
For more details on importing the component configuration, refer to Importing Existing App Example Configuration from Related Links.<Discover Path>\wireless_apps_pic32cxbz3_wbz35\apps\ble\building_blocks\peripheral\deep_sleep_adv\firmware\deep_sleep_adv.X\deep_sleep_adv.mc4Note: Import and Export functionality of the Harmony component configuration will help users to start from a known working setup of the MCC configuration.- Accept dependencies or satisfiers when prompted.
- Verify if the Project Graph
window has all the expected configuration.
Figure 5-100. Project Graph
Developing this Application from scratch using MPLAB Code Configurator
-
Create a new harmony project. For more details, see Creating a New MCC Harmony Project from Related Links.
- In the previous step, the BLE
Stack component is included. Accept all the component auto-activations and
attachment auto-connect confirmations.
Figure 5-101. Auto-Activation and Auto-Connect Request - Include the RCON Component from
the peripheral category.
-
Include the Transparent Service and Transparent Profile component located at :
Harmony-> Wireless->Drivers->BLE. -
Establish the link between the Transparent Service and Profile components.
-
Click Transparent Profile component. In the configuration option, select Enable Server Role.
- Click BLE Stack component.
In the configuration option, select Enable Sleep Mode.
- This action will trigger the auto inclusion of the RTC component. Accept the
activations and auto-connect confirmations.
-
Final Project graph with all the required component.
Verify Advertisement and Component Configuration
This section details the configuration changes needed for each component in accordance with the application use case implementation.
- Select the BLE_Stack
component in the project graph.Note:
Advertising Interval Min can be modified to adjust Deep Sleep Advertising interval.
Tip: Advertisement payload can be configured by user here. - Select Clock
Configuration.
Figure 5-102. Clock Configuration 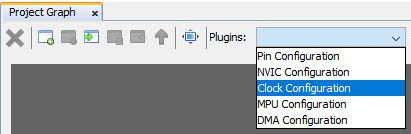
- Configure RTC clock configuration.
Figure 5-103. Clock Configuration Note: Even after enabling and selecting the SOSC as backup source in the clock configuration, the LPCLK and RTC clock still show as 0Hz. This is a known issue which will be resolved in the upcoming MCC release. For the time being, to fix this issue, a manual application code modification is necessary. The required change will be discussed in the next section. - Configure LED GPIO Configuration.
Figure 5-104. Pin Configurations Note:- The above GPIO configuration is used for indicating the device state in this example and is optional.
- The configuration bits will be generated after user Generates Code.
-
Configure RTOS configuration by increasing the Total heap size from the default value.
Figure 5-105. FreeRTOS Configuration
Generate Code
For more details on code generation, refer to MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC) Code Generation from Related Links.
Files and Routines Automatically generated by the MCC
After generating the program source from the MCC interface by clicking Generate Code, the BLE configuration source and header files can then be found in the following project directories.
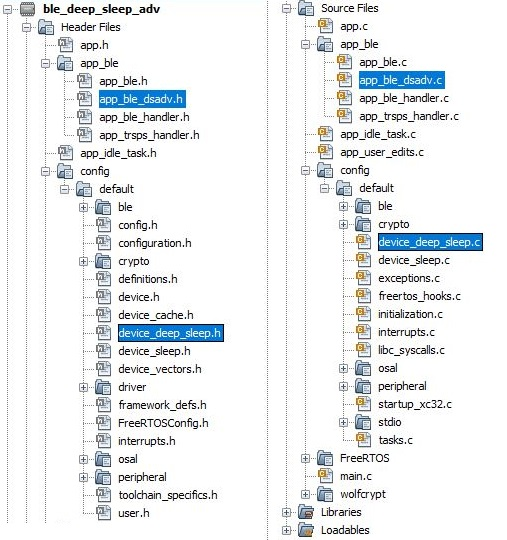
Initialization routines for OSAL, RF System, and BLE System are auto-generated by the MCC. See OSAL Libraries Help in Reference Documentation from Related Links. Initialization routine executed during program initialization can be found in the project file.

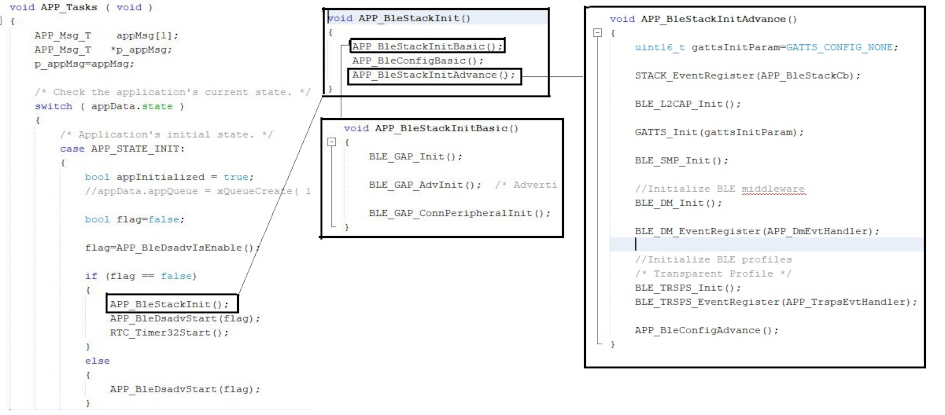
The BLE stack initialization routine executed during Application Initialization can be found in project files. This initialization routine is automatically generated by the MCC. This call initializes and configures the GAP, GATT, SMP, L2CAP and BLE middleware layers.
During system sleep, clock (system PLL) will be disabled and system tick will be turned off. FreeRTOS timer needs to be compensated for the time spent in sleep. RTC timer which works in sleep mode is used to accomplish this. RTC timer will be initialized after BLE stack initialization.
| Source Files | Usage |
|---|---|
app.c | Application State machine, includes calls for Initialization of all BLE stack (GAP,GATT, SMP, L2CAP) related component configurations |
app_ble.c | Source Code for the BLE stack related component configurations, code related to function calls from app.c |
app_ble_handler.c | All GAP, GATT, SMP and L2CAP Event handlers |
app_ble_dsadv.c | Source Code for utilizing the deep sleep advertising functionality |
device_deep_sleep.c | Source Code for deep Sleep and wake up related system configurations |
app.c is autogenerated and has a state
machine-based application code sample. Users can use this template to develop their
own application.Header Files
-
ble_gap.hcontains BLE GAP functions and is automatically included inapp.c
Function Calls
- MCC generates and adds the code to
initialize the BLE Stack GAP, GATT, SMP and L2CAP in
APP_BleStackInit()and the Deep Sleep Advertising functionality inAPP_BleDsadvStart(flag) APP_BleStackInit()andAPP_BleDsadvStart(flag)are the APIs that will be called inside the Applications Initial StateAPP_STATE_INITinapp.c
Manual Application Code Edit
This section talks about the mandatory code modifications that need to be incorporated in order to implement the Deep Sleep Advertising functionality.
app_user_edits.c- Some of the Harmony 3
generated files cannot be fully configured by the MPLAB Code
Configurator. This file contains the instructions for the user to modify
these files.
Follow the instruction mentioned in
app_user_edits.cand after completing the required edits, comment out or remove the #error line
- Some of the Harmony 3
generated files cannot be fully configured by the MPLAB Code
Configurator. This file contains the instructions for the user to modify
these files.
Initialization.c- Comment the code inside
SYS_Initialize function
In the MCC Generated Code, the
CLK_Initialize()and ROM functions are by default present inside theSYS_Initialize()function. The user needs to comment out the code referring toCLK_Initialize()and ROM functions in theSYS_Initialize()function and should addunder _on_reset()function in sameinitialization.cfile.Figure 5-109. CLK_Initialize() - Code Inclusion inside
_on_resetfunctionThe previously commented code inside
SYS_Initilaze()function is included hereCLK_Initialize(); typedef int (*FUNC_PCHE_SETUP)(uint32_t); ((FUNC_PCHE_SETUP)(*(uint32_t*)0xF2D0))((PCHE_REGS->PCHE_CHECON & (~(PCHE_CHECON_PFMWS_Msk | PCHE_CHECON_ADRWS_Msk | PCHE_CHECON_PREFEN_Msk))) | (PCHE_CHECON_PFMWS(2) | PCHE_CHECON_PREFEN(1))); //Set RF as idle mode RF_SetIdleMode(); - Code Inclusion inside
SYS_InitializefunctionDEVICE_DeepSleepWakeSrc_T wakeSrc; DEVICE_GetDeepSleepWakeUpSrc(&wakeSrc); if (wakeSrc == DEVICE_DEEP_SLEEP_WAKE_NONE) //Initialize RTC if wake source is none(i.e power on reset) { RTC_Initialize(); }Figure 5-110. SYS_Initialize
- Comment the code inside
SYS_Initialize function
heap_4.c- Comment the below
code and replace it with the Modified Code inside
heap_4.c(available as part of FreeRTOS>MemMang)
static uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; --> Original Code static uint8_t __attribute__((section (".bss.ucHeap"), noload)) ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ]; -->Modified Code- Comment the below
code and replace it with the Modified Code inside
Plib_rtc.h
Step 4 -
- Default generated:
#define RTC_COUNTER_CLOCK_FREQUENCY (0U / (1UL << (0x1U - 1U))) - Replace to:
#define RTC_COUNTER_CLOCK_FREQUENCY (32768U / (1UL << (0x1U - 1U)))
Step 5 - Plib_clk.c
- To enhance the CLK initialization period for the delay time of polling XTAL and PLL ready, mentioned below are changes that need to be made. This requires a manual code change as the current MCC is not capable of generating the required code.
- MCC Present Setting
- MCC New Settings
//check CLDO ready
while ((CFG_REGS->CFG_MISCSTAT & CFG_MISCSTAT_CLDORDY_Msk) == 0);
//programming 4ms delay - programming subsys_xtal_ready_delay -> Reduce to 2ms
//check xtal spec for delay required
BTZBSYS_REGS->BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG1 = ((BTZBSYS_REGS->BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG1 & ~BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG1_subsys_xtal_ready_delay_Msk)
| ((0x01) << BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG1_subsys_xtal_ready_delay_Pos));
//wait for crystal ready
while((BTZBSYS_REGS->BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_STATUS_REG1 & BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_STATUS_REG1_xtal_ready_out_Msk) != BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_STATUS_REG1_xtal_ready_out_Msk);
// set PLL_enable
BLE_REGS->BLE_DPLL_RG2 &= ~(0x02);
//programming delay for pll lock - 500 us -> Reduce to 64us
//32 us steps - check pll spec for final value
BTZBSYS_REGS->BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG3 = ((BTZBSYS_REGS->BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG3 & ~BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG3_subsys_pll_ready_delay_Msk )
| ((0x02) << BTZBSYS_SUBSYS_CNTRL_REG3_subsys_pll_ready_delay_Pos));
Step 6 - WBZ351.ld
- Additional linker file related changes need to be incorporated to define the backup RAM address. This configuration will be later made available in the MCC configuration. Until then, this manual edit is required.
- The highlighted code in the below image needs to be incorporated to the MCC
generated
WBZ351.ldfile
User Application Development
Include
-
definitions.hmust be included in all the files where port pin macros are used
Note:definitions.his not specific to just port peripheral but instead must be included in all the application source files where any peripheral functionality will be exercised
Enter Deep Sleep mode
-
DEVICE_EnterDeepSleep(false,0);This API can be called to put the device to Deep Sleep mode.
Start Deep Sleep Advertisement
-
APP_BleDsadvStart(false);
This API can be called in
APP_STATE_INITofapp.cto start the Deep Sleep Advertising.Note: Users can explore more BLE Advertisement functionalities using the BLE Stack APIs. For more information, refer to BLE Stack in Reference Documentation from Related Links.
Application Use Case Implementation
This application implementation is purely user choice. It is designed in such a way that the device enters into Deep Sleep mode upon power up and when SW2 is pressed, the device starts the Deep Sleep Advertisements based on the fixed advertisement interval. Device then wakes up from Deep Sleep in regular intervals to start an advertisement and go back to sleep again.
This scenario is implemented by modifying the default generated code inside the
switch case in app.c. User can implement their desired application
workflow by making use of the available function calls.
app.cKnown Issue:
System Sleep implementation source (device_sleep.c) and header
(device_sleep.h) files may sometimes not be included when
generating the project through MCC so follow the below steps to avoid this.
Step1: Uncheck and re-enable the Enable Sleep Mode and Enable Deep Sleep Advertising option inside the BLE Stack component in the project graph as shown in the figure below and accept the dependencies requested.
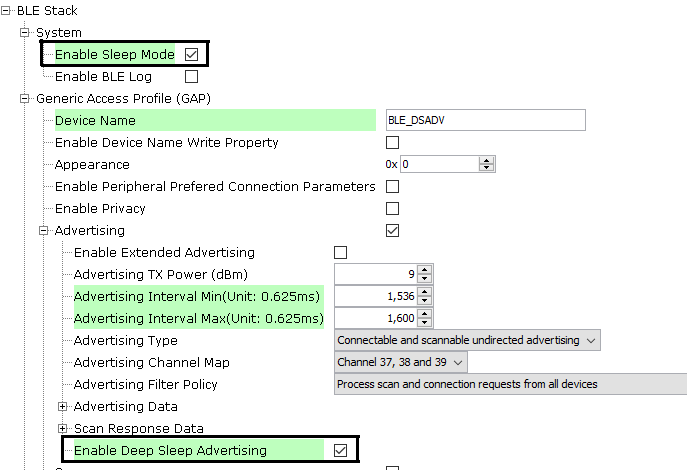
Step2: Click the Force Update on All option and press Generate.
Where to go from here
See BLE Connection from Related Links.
