4.4.4 CFM MEP Configuration
The switch supports two types of MEP: Port Down-MEPs and VLAN Down-MEPs. These MEPs can be configured from the CFM MEP Configuration web page. The following figure shows the CFM MEP configuration table.
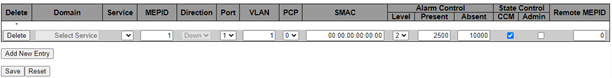
The CFM MEP Configuration page has the following parameters:
Port Down-MEPs
In 802.1Q terminology, Port MEPs are located below the EISS entity, that is, closest to the physical port. Port MEPs are used by, for example, APS for protection purposes. Port MEPs are created when the encompassing service has type Port. Port MEPs may send OAM PDUs tagged or untagged. An OAM PDU is sent untagged only if the MEP's VLAN is set to Inherit (0). Any other value sends it tagged with the port's TPID, whether VLAN matches the port's PVID and that PVID is meant to be sent untagged.
VLAN Down-MEPs
In 802.1Q terminology, VLAN MEPs are located above the EISS entity. This means that tagging of OAM PDUs follows the port's VLAN configuration.
Therefore, if a VLAN MEP is created on the Port's PVID and PVID is configured to be untagged, OAM PDUs are transmitted untagged. VLAN MEPs are created when the encompassing service has type VLAN.
Following are the rules to follow while creating Down-MEPs:
- There can only be one Port MEP on the same port
- There can only be one VLAN MEP on the same port and VLAN
- A VLAN MEP must have a higher MD/MEG level than a Port MEP on the same port and VLAN
- All port MEPs must have the same MD/MEG level
- Any VLAN MEP must have an ME/MEG level higher than a Port MEP
These checks are performed automatically on administratively enabled MEPs. When you change a particular MEP, change the Service Type from Port to VLAN or vice-versa, or change the domain's MD/MEG level.
- Delete: Check to delete the entry. It is deleted during the next save.
- Domain: Name of the domain under which this MEP resides
- Service: Name of the service under which this MEP resides
- MEPID: The identification of this MEP. Must be an integer [1–8091]
- Direction: Set whether this MEP is an Up- or a Down-MEP
- Port: Port on which this MEP resides
- VLAN: VLAN ID. Use the value 0 to indicate untagged traffic (implies a port MEP)
- PCP: Choose PCP value in PDUs' VLAN tag. Not used if untagged.
- SMAC: Set a Source MAC address to be used in CCM PDUs originating at this MEP. This must be a unicast address. Format is XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX. If all-zeros, then the switch port's MAC address is used.
- Alarm Control: Level—if a defect is
detected with a priority higher than this level, a fault alarm notification is generated.
Valid range is [1; 6] with 1 indicating that any defect can cause a fault alarm and 6
indicating that no defect can cause a fault alarm. See 802.1Q-2018, clause 20.9.5,
LowestAlarmPri. The following table lists the possible defects and their priorities.
Table 4-1. List of Defects and Priorities Short Name Description Priority DefRDICCM Remote Defect Indication 1 DefMACstatus MAC Status 2 DefRemoteCCM Remote CCM 3 DefErrorCCM Error CCM Received 4 DefXconCCM Cross Connect CCM Received 5 Present: The time in milliseconds where defects must be present before a fault alarm notification is issued. Default is 2500 ms.
Absent: The time in milliseconds where defects must be absent before a fault alarm notification is reset. Default is 10000 ms.
- State Control: Enable or disable generation of CCMs
- Admin: Enable or disable this MEP. When this MEP is enabled, it checks received/missing CCMs and can raise defects.
