2.3.3.2.2 Content from File
(Ask a Question)Import the memory client from a memory file with this option. Click Browse to navigate to the location of the memory file and import. Select the Memory File and click Open.
*.mem file is
selected.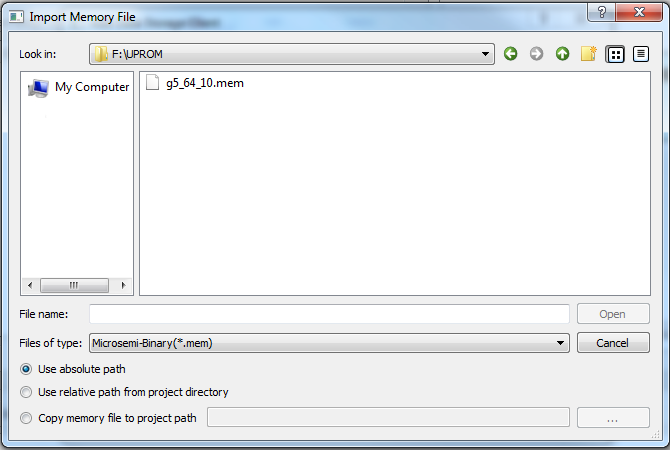
Use Absolute Path
When this is selected, the absolute path of the memory file appears in the Content from File field.
Use Relative Path from Project Directory
When this is selected, the Relative Path of the Memory File (relative to the Project location) is displayed in the Content from File field.
Copy Memory File to Project Path
Select this option and click Browse to navigate to the location of the memory file to copy from. The memory file is copied to the project location.
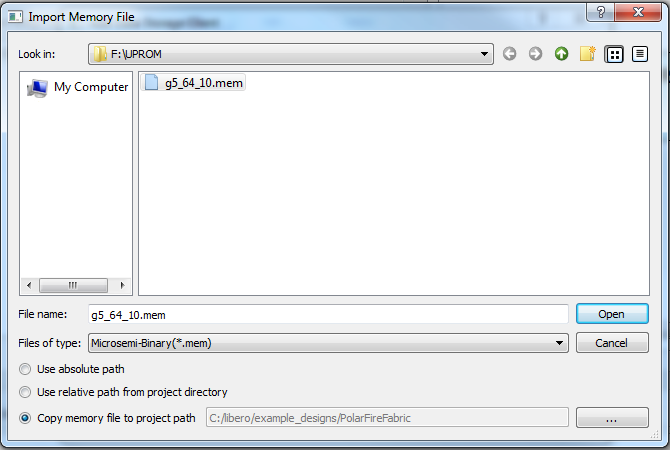
The memory file cannot be copied to and stored in the project's
subfolders: component, smartgen, synthesis, designer, simulation, stimulus, tool data, and
constraint. To prevent users from inadvertently copying the memory file into these
sub-folders, these project subfolders are hidden from view when you select the project
folder. Copy the memory file to the same project folder as the *.prjx
file.
(*.hex, *.ihx),
Motorola-S (*.s), Simple-Hex (*.shx), and
Microsemi-Binary (*.mem) memory file formats. For more information about
the supported memory file formats, see Appendix: Supported Memory File Formats for LSRAM and μSRAM.*.mem is used. The
*.mem file must meet the following requirements:- Each row is one 9-bit binary word (only 0s and 1s).
- The number of rows in the file (word count) must be less than or equal to the memory space of the μPROM (up to 58,368 words).
- The memory file must have the
*.memfile extension. The following figure shows an example memory file.Figure 2-43. Microsemi Binary File (*.mem) Example
