4.13.1 Spanning Tree Bridge Settings Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and its Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) variations are used mainly for the following reasons:
- To prevent possible network loops, which cause broadcast storming without STP
- To offer redundancy path from Switch to Switch or path to path over multiple switches by supporting network loops under the control of STP. The STP algorithm ensures that at any given time, only one path out of multiple possible loops is active, allowing the switch to use multiple backup paths if the main connection path goes down.
The following figure shows the STP Bridge configuration details.
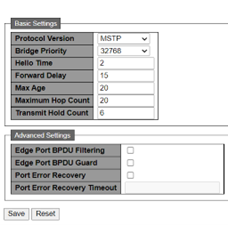
The STP Bridge Configuration page has the following parameters:
- STP Bridge Configuration
- Protocol Version: The
following spanning tree protocols are supported:
- MSTP
- RSTP
- STP
- Bridge Priority: Controls the bridge priority. Lower numeric values have better priority. The bridge priority plus the Multiple Spanning Tree Instance (MSTI) number, concatenated with the 6-byte MAC address of the switch forms a Bridge Identifier. For MSTP operation, this is the priority of the CIST. Otherwise, this is the priority of the STP/RSTP bridge.
- Forward Delay: The delay used by STP Bridges to transit Root and Designated Ports to Forwarding (used in STP compatible mode). Valid values are in the range of 4s–30s.
- Maximum Age: The maximum age of the information transmitted by the Bridge when it is the Root Bridge. Valid values are in the range 6s–40s, and maximum age must be ≤ (FwdDelay−1) * 2.
- Maximum Hop Count: This defines the initial value of remaining Hops for MSTI information generated at the boundary of an MSTI region. It defines how many bridges a root bridge can distribute its BPDU information to. Valid values are in the range of 6 to 40 hops.
- Transmit Hold Count: The number of BPDUs a bridge port can send per second. When exceeded, transmission of the next BPDU is delayed. Valid values are in the range 1–10 BPDUs per second.
- Protocol Version: The
following spanning tree protocols are supported:
- Advanced Settings
- Edge Port BPDU Filtering: Control whether a port explicitly configured as Edge transmits and receives BPDUs.
- Edge Port BPDU Guard: Control whether a port explicitly configured as Edge disables itself upon reception of a BPDU. The port enters the error-disabled state and is removed from the active topology.
- Port Error Recovery: Control whether a port in the error-disabled state is automatically enabled after a certain time. If recovery is not enabled, ports must be disabled and re-enabled for normal STP operation. The condition is also cleared by a system reboot.
- Port Error Recovery Timeout: The time to pass before a port in the error-disabled state can be enabled. Valid values are between 30s–86400s (24 hours).
