3.2.6.1 Wi-Fi Service
The MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC) allows Wi-Fi service configuration as mentioned
below:
- Station mode
- Soft AP mode
This section allows Wi-Fi service configuration as mentioned below:
- Wi-Fi Modes: Drop-down to
select Wi-Fi modes.
Available options are:
- StationMode
- ProvisionMode
- SoftAPmode
- Provision Method: Drop-down to
select Wi-Fi Provisioning method.
Available options are:
- Mobile App
- Web Server
- SSID: Wi-Fi Access Point/Network Name
- Passphrase: Wi-Fi Access point/Network password
- Security Type: Wi-Fi security protocol
- Auto Connect : Enable to automatically connect to the AP when the device is in station mode. It shoule be enabled when the device is in AP mode (It should be enabled in all the three modes).
- Provision Callback Handler: Configure callback function name for Wi-Fi Provisioning states (Applicable only if selected Wi-Fi Mode is ProvisionMode)
- WiFi-Callback Handler:
Configure callback function name to handle Wi-Fi service specific events (for
example, Wi-Fi STA connection and disconnection, DHCP resolution, Wi-Fi Scan
indication)
Wi-Fi System Service MCC Configuration
-
Figure 3-31. Wi-Fi Settings: StationMode 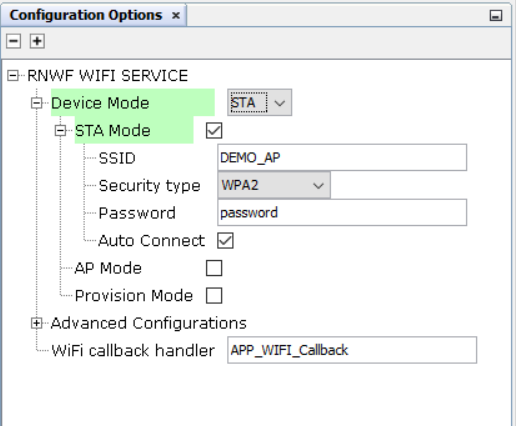
-
Figure 3-32. Wi-Fi Settings: APmode 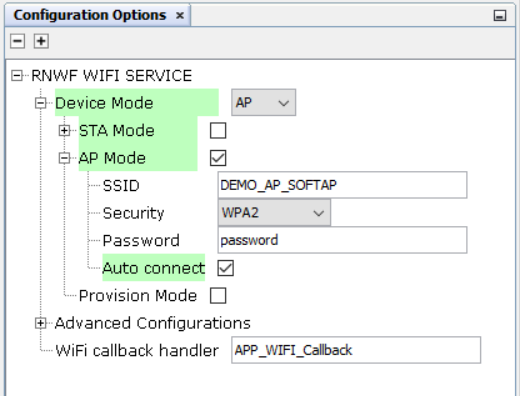
-
Figure 3-33. Wi-Fi Settings: ProvisionMode 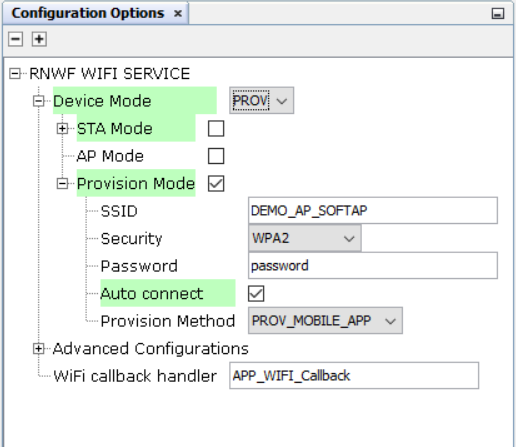
- The Wi-Fi Service API
prototype is as
follows:
SYS_RNWF_RESULT_t SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl( SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SERVICE_t request, void *input)It handles following services and reports the result to application over the return code or through the registered callback.Table 3-17. Wi-Fi Services Option/Command Input Description SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_PARAMSMode, SSID, Passphrase, Security, Autoenable Configures the provided Wi-Fi details and Triggers the connection based on auto enable flag SYS_RNWF_STA_CONNECTNone Triggers the Wi-Fi STA connection SYS_RNWF_STA_DISCONNECTNone Disconnects the connection SYS_RNWF_AP_DISABLENone Disables the SoftAP mode SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_AP_CHANNELChannel number Configure the Wi-Fi channel SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_BSSIDBSSID of AP (String) Configure the Access point's BSSID to which RNWF needs to connect SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_TIMEOUTSeconds (int) Configure Wi-Fi connection timeout SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_HIDDEN,true or false Configure Hidden mode SSID in SoftAP mode SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PASSIVE_SCANNone Request/Trigger Wi-Fi passive scan SYS_RNWF_WIFI_ACTIVE_SCANNone Request/Trigger Wi-Fi active scan SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SET_CALLBACKCallback Function handler Register the call back for async events
-
The following list captures the Wi-Fi callback event codes and their arguments.
| Event | Response Components | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SYS_RNWF_CONNECTED | Association ID:
Integer Connected State: Integer | Wi-Fi connected event code. Reports the connection's Association ID and connected state |
SYS_RNWF_DISCONNECTED | Association ID:
Integer Connected State: Integer | Wi-Fi disconnected event code |
SYS_RNWF_CONNECT_FAILED | Fail event code: Integer | Wi-Fi connection failure event code |
SYS_RNWF_DHCP_DONE | DHCP IP: String | Wi-Fi DHCP complete event code |
SYS_RNWF_SCAN_INDICATION | RSSI: Received signal
strength Sec Type (Int): Recommended security type to use connecting to this AP (10 options) Channel (Int): Channel # of device | Scan results to report each scan list |
SYS_RNWF_SCAN_DONE | None | Scan complete event code |
The following figure illustrates the Station mode connection sequence.
Figure 3-34. Station Mode
Connection Sequence 
Following is the example of establishing connection in the Station mode.
#include <stdio.h> #include <rnwf_wifi_service.h> /* Application Wifi Callback Handler function */ static void SYS_RNWF_WIFI_CallbackHandler ( SYS_RNWF_WIFI_EVENT_t event, uint8_t *p_str) { switch(event) { /* Wi-Fi connected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_CONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Wi-Fi Connected \r\n"); break; } /* Wi-Fi disconnected event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_DISCONNECTED: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("Wi-Fi Disconnected\nReconnecting... \r\n"); SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_STA_CONNECT, NULL); break; } /* Wi-Fi DHCP complete event code*/ case SYS_RNWF_DHCP_DONE: { SYS_CONSOLE_PRINT("DHCP IP:%s\r\n", &p_str[2]); break; } default: { break; } } } /* Application Initialization function */ void APP_Initialize ( void ) { /* Place the App state machine in its initial state. */ g_appData.state = APP_STATE_INITIALIZE; } /* Maintain the application's state machine. */ void APP_Tasks ( void ) { switch(g_appData.state) { /* Application's state machine's initial state. */ case APP_STATE_INITIALIZE: { DMAC_ChannelCallbackRegister(DMAC_CHANNEL_0, APP_RNWF_usartDmaChannelHandler, 0); SYS_RNWF_IF_Init(); g_appData.state = APP_STATE_REGISTER_CALLBACK; break; } /* Register the necessary callbacks */ case APP_STATE_REGISTER_CALLBACK: { /* RNWF Application Callback register */ SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SET_CALLBACK, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_CallbackHandler); /* Wi-Fii Connectivity */ SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PARAM_t wifi_ap_cfg = {SYS_RNWF_WIFI_MODE_AP, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PROV_SSID, SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PROV_PWD, SYS_RNWF_PROV_SECURITY,SYS_RNWF_WIFI_PROV_AUTOCONNECT}; SYS_RNWF_WIFI_SrvCtrl(SYS_RNWF_SET_WIFI_PARAMS, &wifi_ap_cfg); g_appData.state = APP_STATE_TASK; break; } /* Run Event handler */ case APP_STATE_TASK: { SYS_RNWF_IF_EventHandler(); break; } default: { break; } } }
