3.6.4.15 USB I2C Click Example on SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit
Description
This example demonstrates how to use the SERCOM-I2C peripheral in client mode on SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit using USB I2C Click board.
This example uses the I2C peripheral library in client mode and emulates an EEPROM of 512 bytes. The emulated EEPROM consists of two pages, each of size 256 bytes. The I2C client expects two bytes of memory address from the I2C host (USB I2C Click) and the memory address can range from 0x00 to 0x1FF. The following operation can be made on the I2C client (emulated EEPROM).
Byte Write: The I2C host sends the client address, followed by two bytes of the memory address. The client writes the provided data at the given memory address.
Page Write: A page write is initiated the same way as a byte write, but the I2C host can write up to 256 bytes (1 page). If the I2C host sends more than 256 bytes to the I2C client, the memory address will “roll over,” and previous data will be overwritten. During writing, the address “rollover” is from the last byte of the current page to the first byte.
Read Operation: Reads the requested number of bytes from the start address of emulated EEPROM (i.e. 0x00 and the maximum 512 bytes can be read).
Modules/Technology Used
- Peripheral Modules:
- NVMCTRL
- PORT
- SERCOM (I2C)
Hardware Used
Software/Tools Used
This project has been verified to work with the following versions of software tools:
Refer Project Manifest present in harmony-manifest-success.yml under the project folder firmware/src/config/sam_e51_cnano.
- Refer the Release Notes to know the MPLAB X IDE and MCC Plugin version.
- Download and Install MCP2221 I2C SMBus Terminal in the PC.
Because Microchip regularly updates tools, occasionally issue(s) could be discovered while using the newer versions of the tools. If the project does not seem to work and version incompatibility is suspected. It is recommended to double-check and use the same versions that the project was tested with. To download original version of MPLAB Harmony v3 packages, refer to document How to Use the MPLAB Harmony v3 Project Manifest Feature (DS90003305).
Setup
- Connect the SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit to the Host PC as a USB Device through a Type-A male to micro-B USB cable connected to Micro-B USB (Debug USB) port.
- Mount MikroElektronika USB I2C Click over mikroBUS socket #1 on the SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit.
- Connect the MikroElektronika USB I2C Click to the Host PC as a USB Device through a
Type-A male to mini-B USB cable connected to mini-B USB port.
Programming Hex File
The pre-built hex file can be programmed by following the below steps.
- Open MPLAB X IDE.
- Close all existing projects in IDE, if any project is opened.
- Go to File -> Import -> Hex/ELF File.
- In the Import Image File
window,
- Create Prebuilt Project,
- Click the Browse button to select the prebuilt hex file.
- Select Device as ATSAME51J20A.
- Ensure the proper tool is selected under Hardware Tool and click on Next button.
- Select Project Name and Folder,
- Select appropriate project name and folder and click on Finish button
- Create Prebuilt Project,
- In MPLAB X IDE, click on Make and Program Device button to program the device.
- Follow the steps in Running the Demo section below.
Programming/Debugging Application Project
- Open the project (apps/sam_e51_cnano/same51n_mikroe_click/usb_i2c/firmware/sam_e51_cnano.X) in MPLAB X IDE
- Ensure SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit is selected as hardware tool to program/debug the application
- Build the code and program the device by clicking on the Make and Program button in MPLAB X IDE tool bar
- Follow the steps in Running the Demo section below
Running the Demo
- Open MCP2221 I2C SMBus
Terminal Application. If the MCP2221 board is recognized, the user should see
the Select Device field populated with the component ID on the far upper-right
corner of the window:Note: If there is no device ID on that field, refer to the MCP2221 terminal installation instructions to install the board.
- Select File > Import
Commands. Navigate to the project solution folder and select the file MCP2221
- CMDs For I2C Client Demo.csv:
The user should have the following commands listed under the Command list:
- Step 1: Read 512 bytes from I²C
ClientAfter the Terminal is configured, issue the first command on the list by pressing the button Send on the right side. This command accesses the I²C device address 0x54, which is the Client address selected for this example, and reads the 512 bytes data. This is the emulated EEPROM buffer on which the read and write operations are executed.
- Step 2: Write 8 bytes to I²C
Client
- Step 3: Read 8 bytes from I²C
Client
- Step 4: Write 16 bytes to I²C
Client
- Step 5: Read 16 bytes from I²C
Client
- Step 6: Read 512 bytes from I²C
Client
- Step 7: Write page 1 (256bytes) to
I²C Client
- Step 8: Read two pages (256bytes)
from I²C Client
- Step 9: Write page 2 (256bytes) to
I²C Client
- Step 10: Read two pages (256bytes)
from I²C Client
- Step 11: Issue the following
commands and observe output
- Write 1 byte to page 1 address 0x1E.
- Write 1 byte to page 2 address 0x1E.
- Read two pages. Check whether
above bytes are written properly.
Instructions to Add USB I2C Functionality to the Application
The user could use this demonstration as an example to add USB I2C functionality to the MPLAB Harmony v3 based application. Follow the below steps.
- If the user has not downloaded the USB I2C demo yet Click Here to download, otherwise go to next step.
- Unzip the downloaded .zip file.
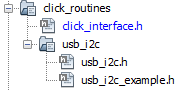
- From the unzipped folder usb_i2c/firmware/src, copy the folder click_routines to the folder firmware/src under the MPLAB Harmony v3 application project.
- Open MPLAB X IDE.
- Open the application project.
- In the project explorer, right click on
folder Header Files and add a sub folder click_routines by selecting
Add Existing Items from Folders...
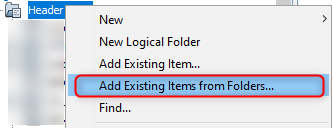
- Click on Add Folder... button.
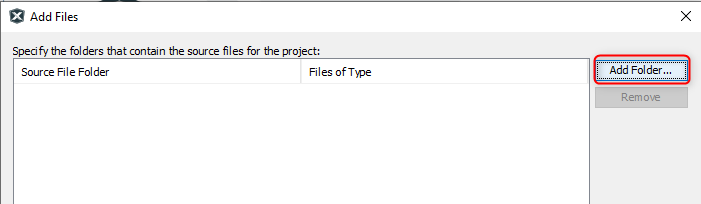
- Select the click_routines folder and select Files of Types as Header
Files.
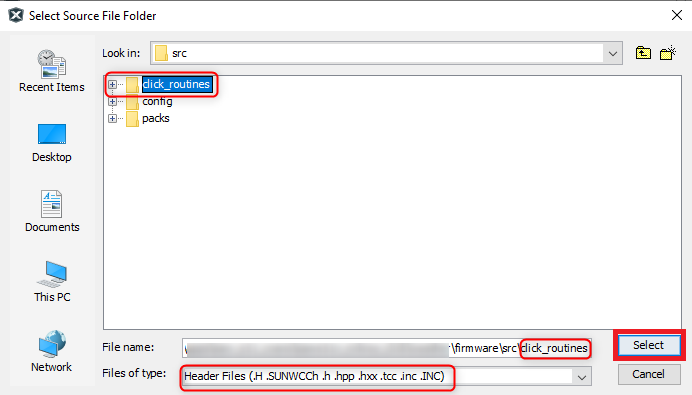
- Click on Add button to add the selected folder.
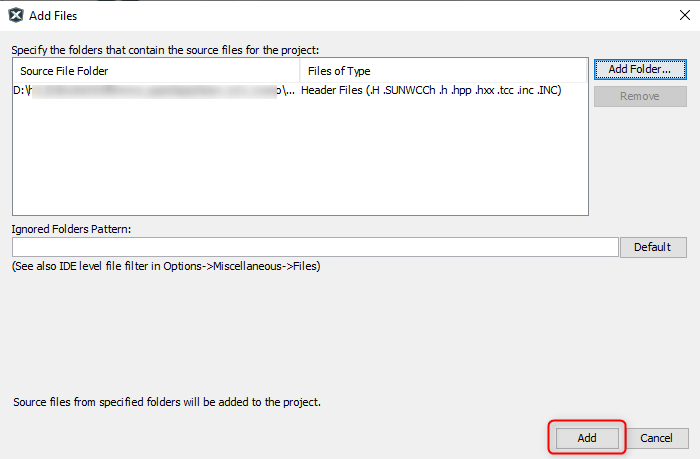
- The USB I2C click example
header files gets added to the project.
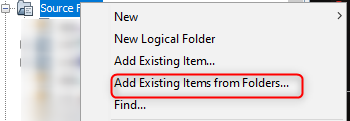
- In the project explorer, right click on folder Source Files and add a sub
folder click_routines by selecting Add Existing Items from Folders...
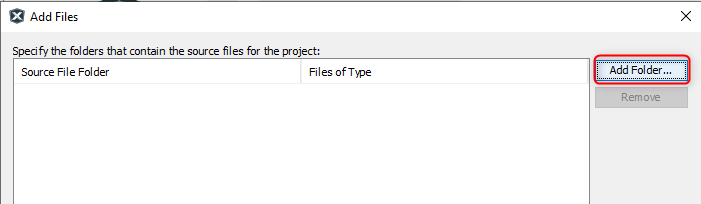
- Click on Add Folder... button.
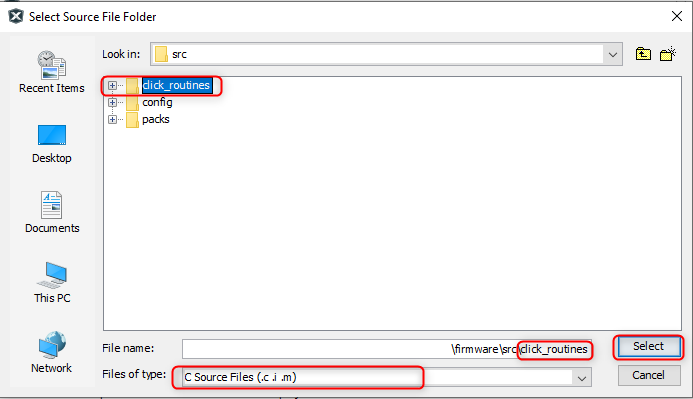
- Select the click_routines folder and select Files of Types as Source
Files.
- Click on Add button to add the selected folder.
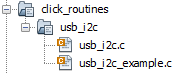
- The USB I2C click example
source files gets added to the project.
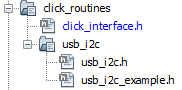
- The USB I2C click example
uses the I2C peripheral. The configuration of this peripheral for the
application depends on the 32-bit MCU and development board the user is using.
- Configure I2C:
- Add the I2C peripheral block to the MCC project graph.
- Configure I2C Pins
using MCC Pin configuration Window.The I2C configuration depends on:
- 32-bit MCU
- 32-bit MCU development board
-
The socket on which the user has mounted the USB I2C click board
Example: The USB I2C click example on SAM E51 Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit uses mikroBUS socket #1 on the Curiosity Nano Base for Click boards to mount the USB I2C click board. The I2C lines from MCU coming to this socket are from the SERCOM4 peripheral on the MCU.
Figure 3-52. MCC Project Graph - I2C Configuration Figure 3-53. MCC Pin Configurator - I2C Pin Configuration
- Map Generic Macros:
- After generating the project, following the above configuration, map the generic macros used in the click routines to the Harmony PLIB APIs of the 32-bit MCU the project is running on.
- The generic macros should be
mapped in the header file click_interface.h.

The click_routines folder contain an example C source file usb_i2c_example.c. The user could use usb_i2c_example.c as a reference to add USB I2C functionality to the application.
- Configure I2C:
Comments
-
Reference Training Module:
- This application demo builds and
works out of box by following the instructions above in Running the Demo
section. If the user needs to enhance/customize this application demo, should use the
MPLAB Harmony v3 Software framework. Refer links below to setup and build the
applications using MPLAB Harmony.
- How to Setup MPLAB Harmony v3 Software Development Framework (DS90003232).
- How to Build an Application by Adding a New PLIB, Driver, or Middleware to an Existing MPLAB Harmony v3 Project (DS90003253).
- Video - How to Set up the Tools Required to Get Started with MPLAB® Harmony v3 and MCC
- Create a new MPLAB Harmony v3 project using MCC
- Update and Configure an Existing MHC-based MPLAB Harmony v3 Project to MCC-based Project
