1.1.5 SpaceWire Peripheral Library (SPW)
The SpaceWire (SpW) module provides support for transmission of any type of protocol or data structure using SpaceWire packets. It has hardware support for logical addressing, execution of incoming RMAP commands, and for reception/generation of Escape Characters (Broadcast Codes) and Time Codes.
Configuring the library
Configure the peripheral library using the MHC.
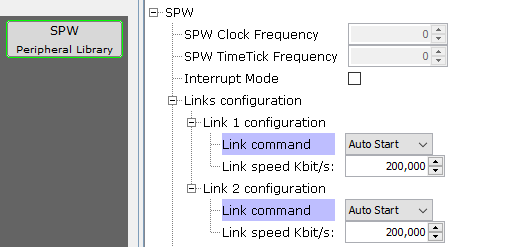
"Interrupt Mode" option can be enabled to add interface functions for interrupt support (Enable, Disable and callback register).
For each link, set the default command mode and bit rate.
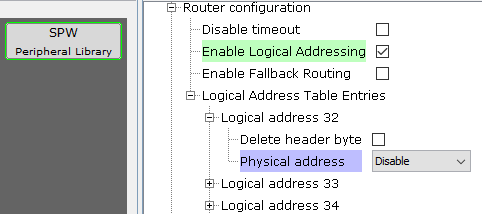
Configure the router and set logical address routing in table.
"Disable timeout": Disable the default timeout on destination address stall.
"Enable Logical Addressing" : Check to enable router logical addressing.
"Enable Fallback routing" : Enable the fallback routing if the addressed destination is unavailable. (only applicable with logical addressing)
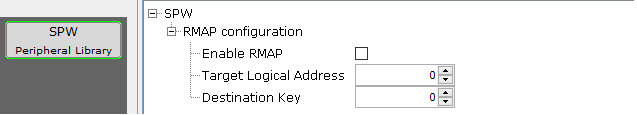
Enable and configure the RMAP module to accept/reject commands automatically.
"Target Logical Address" : Any incoming RMAP command must have a TLA matching this value, or TLA = 0xFE, in order to be accepted.
"Destination Key" : Any incoming RMAP command must have a matching Destination Key in order to be accepted.
Using the library
The SPW initialization is done during system initialization. It configure the module depending on the given parameters in MHC interface.
If interrupts are used, the callback function should be set and expected interrupts enabled:
/* Add SPW interrupt callback */
SPW_CallbackRegister(SPW_Callback_Function, (uintptr_t)NULL);
/* Enable SPW Link interrupts */
SPW_LINK_InterruptEnable(SPW_LINK_1 , SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_DISERR |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_PARERR |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_ESCERR |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_CRERR |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_LINKABORT |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_EEPTRANS |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_EEPREC |
SPW_LINK_INT_MASK_DISCARD);
/* Enable packet TX interrupts */
SPW_PKTTX_InterruptEnable(SPW_PKTTX_INT_MASK_DEACT);
/* Enable packet TX interrupts */
SPW_PKTTX_InterruptEnable(SPW_PKTTX_INT_MASK_DEACT);Link State
For both link, the current state can be checked with SPW_LINK_StatusGet
Example for waiting both links to be in Run state:
/* Wait link goes to Run state */
SPW_LINK_STATE spwLink1Status = 0;
SPW_LINK_STATE spwLink2Status = 0;
do
{
spwLink1Status = SPW_LINK_GET_STATE(SPW_LINK_StatusGet(SPW_LINK_1));
spwLink2Status = SPW_LINK_GET_STATE(SPW_LINK_StatusGet(SPW_LINK_2));
}
while ( (spwLink1Status != SPW_LINK_STATE_RUN) &&
(spwLink2Status != SPW_LINK_STATE_RUN) );Link Distributed interrupts
For both link, distributed interrupt and distributed interrupt acknowledge can be enabled and disable using functions:
SPW_LINK_DistInterruptEnableandSPW_LINK_DistInterruptDisablefor distributed interrupt.SPW_LINK_DistAckInterruptEnableandSPW_LINK_DistAckInterruptDisablefor distributed interrupt acknowledge.
If interrupts are used, the callback function should be set and expected interrupts enabled.
/* Enable Link 1 distributed interrupt for values 2 and 8 */
SPW_LINK_DistInterruptEnable(SPW_LINK_1, SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D2 | SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D8);
/* Enable Link 2 distributed interrupt for values 2 and 8 */
SPW_LINK_DistInterruptEnable(SPW_LINK_2, SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D2 | SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D8);
/* Enable Link 1 distributed interrupt acknowledge for values 2 and 8 */
SPW_LINK_DistAckInterruptEnable(SPW_LINK_1, SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D2 | SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D8);
/* Enable Link 2 distributed interrupt acknowledge for values 2 and 8 */
SPW_LINK_DistAckInterruptEnable(SPW_LINK_2, SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D2 | SPW_LINK_DIST_ACK_MASK_D8);The interrupt status can be read and clear using the functions:
SPW_LINK_DistIrqStatusGetMaskedAndClearfor distributed interrupt.SPW_LINK_DistAckIrqStatusGetMaskedAndClearfor distributed interrupt acknowledge.
Link escape character matching events
For each link, two escape character matching event can be configured using SPW_LINK_EscapeCharEvent1Set and SPW_LINK_EscapeCharEvent2Set functions.
/* Set link 2 escape character match event 1 for time code 0x22 */
SPW_LINK_EscapeCharEvent1Set(SPW_LINK_2, true, 0xFF, 0x22);Matching event generate an interrupt. The matching escape character can then be read using the functions SPW_LINK_LastRecvEscapeCharEvent1Get or SPW_LINK_LastRecvEscapeCharEvent2Get.
Link transmit escape character
Escape character can be transmit from both link using the function SPW_LINK_TransmitEscapeChar
/* Transmit escape character (time code 0x22) on link 1 */
SPW_LINK_TransmitEscapeChar(SPW_LINK_1, 0x22);Router configuration and status
The router configuration is done during system initialization and it can be also modified by the application:
Timeout can be enable or disable with
SPW_ROUTER_TimeoutDisablefunctionFall back option can be enable or disable with
SPW_ROUTER_FallbackEnablefunctionLogical address routing can be modified with
SPW_ROUTER_RoutingTableEntrySetfunction.
The router status can be get using the function SPW_ROUTER_StatusGet and timeout status with SPW_ROUTER_TimeoutStatusGet
Packet reception
The receiver can receive SpaceWire packets if the routing mechanism is set up to reach them, i.e., if the logical address or logical path is correctly set.
The received buffers have 3 state:
NEXT: The Rx buffers are set up.
CURRENT: The Rx buffers collect SpaceWire packets.
PREVIOUS: The data collected and stored in memory can be read.
Set a buffer in NEXT state
Receive buffer can be set in NEXT state using the function SPW_PKTRX_SetNextBuffer. Parameters are :
The data buffer pointers that will contains the received packet and his size in bytes.
The packet information buffer pointer and the number of packet that can be received.
The split option to indicate if incoming packet should be split when this buffer activates.
The start condition and the matching value for start condition if needed.
/* Allocate Rx buffer of data */
uint8_t __attribute__((aligned (32)))__attribute__((section (".ram_nocache"))) buffer_data[PACKET_SIZE_BYTES] = {0};
/* Allocate Rx packet information list */
SPW_PKTRX_INFO __attribute__((aligned (32)))__attribute__((section (".ram_nocache"))) packet_info[PACKET_NUMBER] = {0};
// Set buffer in Next buffer with start condition now
SPW_PKTRX_SetNextBuffer(
&(buffer_data[0]),
sizeof(buffer_data),
&(packet_info[0]),
PACKET_NUMBER,
false,
SPW_PKTRX_NXTBUF_START_NOW,
0);Get receiver status
The status for NEXT, CURRENT and PREVIOUS buffers can be get with SPW_PKTRX_StatusGet to check or wait transitions. For example, wait buffer become active after he was set in next buffer:
/* Wait buffer become active */
while ((SPW_PKTRX_StatusGet() & SPW_PKTRX_STATUS_ACT) == 0);Deactivate CURRENT buffer: Split or Discard
The CURRENT buffer automatically deactivates if:
The CURRENT buffer (information) is full and the PREVIOUS one is not locked.
The CURRENT buffer (data) is full and the PREVIOUS one is not locked. In this case, the on-going packet is split.
The starting condition of the next buffer is matched and the PREVIOUS one is not locked
The user can also request the CURRENT buffer to deactivate in two ways:
Split request with function
SPW_PKTRX_CurrentPacketSplitif the PREVIOUS buffer is not lockedAbort of the CURRENT reception with function
SPW_PKTRX_CurrentPacketAbort, in that case it discards any ongoing packet.
/* Deactivate current buffer (Abort with split) */
SPW_PKTRX_CurrentPacketSplit();Get PREVIOUS status to unlock the buffer
The status of the previous buffer can be gets with function ``SPW_PKTRX_GetPreviousBufferStatus````. Reading his status also unlock the PREVIOUS buffer.
/* Get Status and unlock previous buffer */ SPW_PKTRX_PREV_STATUS status = SPW_PKTRX_GetPreviousBufferStatus();
Packet transmission
SpaceWire packets are transmitted by the packet transmit block to the SpaceWire network, passing through the router block. Send list with multiple entries are used to transfer data SpaceWire packets. Each entry describe the elements in the packet that will be sent:
Routing bytes
Escape characters
Header pointer, size and CRC option.
Data pointer, size and CRC option.
Send lists go through three states:
NEXT: The transmit send lists are set up.
CURRENT: The send list is sent over the SpaceWire network.
PREVIOUS: All the data has been transferred to the network and the status of the send list can be read.
Set a send list in NEXT state
Send list can be set in NEXT state using the function SPW_PKTTX_SetNextSendList. Parameters are:
The routing table pointer for the 4 routing bytes. If they differ from 0, those will be the start of each packet in the Send List. All bytes are set to 0 if this pointer is NULL.
The send list buffer pointers and the number of entries to be sent.
The abort option if ongoing send list should be abort when this send list wants to start.
The start condition and the matching value for start condition if needed.
/* Allocate Tx buffer for header */
uint8_t __attribute__((aligned (32)))__attribute__((section (".ram_nocache"))) header_buffer[HEADER_SIZE_BYTES] = {0};
/* Allocate Tx buffer for data */
uint32_t __attribute__((aligned (32)))__attribute__((section (".ram_nocache"))) tx_data_buffer[DATA_SIZE_WORDS] = {0};
/* Allocate Tx send list */
SPW_PKTTX_SEND_LIST_ENTRY __attribute__((aligned (32)))__attribute__((section (".ram_nocache"))) packet_send_list[NUM_PACKET] = {0};
// Prepare send list
packet_send_list[0].RSize = 1;
packet_send_list[0].RB1 = SPW_ROUTER_LINK0_PORT;
packet_send_list[0].EscMask = 0xF;
packet_send_list[0].EscChar = 0xFA;
packet_send_list[0].HCrc = 1;
packet_send_list[0].HSize = HEADER_SIZE_BYTES;
packet_send_list[0].HAddr = (unsigned int ) &(header_buffer[0]);
packet_send_list[0].DCrc = 1;
packet_send_list[0].DSize = DATA_SIZE_WORDS * 4;
packet_send_list[0].DAddr = (unsigned int) &(tx_data_buffer[0]);
// Set NEXT send list without router bytes.
SPW_PKTTX_SetNextSendList(
NULL,
&(_packet_send_list[0]),
NUM_PACKET,
true,
SPW_PKTTX_NXTSEND_START_NOW,
0);Get transmitter status
The status for NEXT, CURRENT and PREVIOUS buffers can be get with SPW_PKTTX_StatusGet.
The field SPW_PKTTX_STATUS_PREV_MASK contains the PREVIOUS send list status.
/* Get transmitter Status */
SPW_PKTTX_STATUS tx_status = SPW_PKTTX_StatusGet();
/* Get PREVIOUS status */
SPW_PKTTX_PREV previous = SPW_PKTTX_STATUS_PREV_GET(tx_status);Unlock PREVIOUS
The PREVIOUS send list should be unlocked by performing a dummy write in status register. This can be done with the function SPW_PKTTX_UnlockStatus:
/* Unlock previous buffer status */
SPW_PKTTX_UnlockStatus();RMAP get Status
RMAP status can be check with SPW_RMAP_StatusGetAndClear function. It can be used to check if there was an error during the processing of a received RMAP command.
/* Get and clear RMAP status */
SPW_RMAP_STATUS status = SPW_RMAP_StatusGetAndClear();
/* Get ERROR code */
SPW_RMAP_ERRCODE error_code = SPW_RMAP_STATUS_GET_ERRCODE(status);Time Code Handler
The time code handler (TCH) receives and transmits time codes over multiple SpaceWire interfaces. It operates either in Host mode where it is the source of time codes, or in Client mode where it is driven by incoming time codes.
configure Sender and Listener links
To select interfaces were time code should be transmitted to or received from using the functions SPW_TCH_LinkListenerSet and SPW_TCH_LinkSenderSet
/* Configure TCH to send Time Code on Link 1 */
SPW_TCH_LinkSenderSet(SPW_TCH_SEL_LINK_MASK_L1);configure Event Source
The event source that drives the time codes is configured using the function SPW_TCH_ConfigureEvent
/* Configure TCH event source on RTCOUT0 event */
SPW_TCH_ConfigureEvent(SPW_SYNC_EVENT_MASK_RTCOUT0);TCH Restart
The SPW_TCH_ConfigureRestart function can be used to restart the current value of the Time Code, restart value can be configured to be set either :
Only once to set a value on next input source event.
Periodically at each input source event.
/* Configure TCH restart at 0 on each PPS event (1 pulse per second) */
SPW_TCH_ConfigureRestart(0, false, SPW_TCH_CFG_RESTART_IN_PPS, 0);Time Code Event notification
To react on any valid time code, the time code event interrupt can be used. The function SPW_TCH_ConfigureTcEvent can be used to set the mask and values. To trigger an interrupt, for any bit set in the mask the corresponding bit in the time code and the value must be equal.
/* Configure Time Code Event to match time code '0x10' */
SPW_TCH_ConfigureTcEvent(0xFF, 0x10);Time Code Watchdog
A watchdog notification can be set up to detect whether a time code arrives in the expected time window. This is
typically only used in Client mode. Early and late watchdog indications can be programmed with the function SPW_TCH_ConfigureWatchdog.
They both works independently and will trigger dedicated interrupt when:
If a time code arrives before the programmed number of ticks of TimeTick clock.
If no time code arrives before the programmed number of ticks of TimeTick clock.
Get or select Time Code
The last Time Code distributed value can be read using the function SPW_TCH_LastTimeCodeGet
The next Time Code value to distribute can be set manually : To select Time Code N to be transmitted, write N-1 with the function SPW_TCH_LastTimeCodeSet before the configured event.
To run Host mode manually from software without an event source, the function SPW_TCH_LastTimeCodeSet can be used with the parameter now to true each time a time code should be sent.
/* Manually send time code '0x04' now */
SPW_TCH_LastTimeCodeSet(0x04, true);Time Code Interrupts
TCH interrupts can be enabled and disable using functions SPW_TCH_InterruptEnable and SPW_TCH_InterruptDisable
If interrupts are used, the callback function should be set and expected interrupts enabled.
/* Enable SPW TCH interrupts */
SPW_TCH_InterruptEnable(SPW_TCH_INT_MASK_TCEVENT | SPW_TCH_INT_MASK_TIMECODE);The TCH interrupt status can be read and clear using the function SPW_TCH_IrqStatusGetMaskedAndClear
